Page 81 - MODERN ELECTROCHEMISTRY
P. 81
ELECTROCHEMISTRY 25
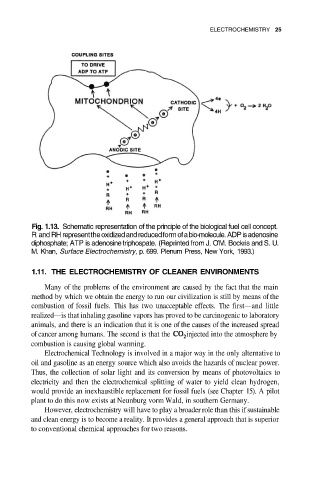
Fig. 1.13. Schematic representation of the principle of the biological fuel cell concept.
R and RH represent the oxidized and reduced form of a bio-molecule. ADP is adenosine
diphosphate; ATP is adenosine triphospate. (Reprinted from J. O’M. Bockris and S. U.
M. Khan, Surface Electrochemistry, p. 699. Plenum Press, New York, 1993.)
1.11. THE ELECTROCHEMISTRY OF CLEANER ENVIRONMENTS
Many of the problems of the environment are caused by the fact that the main
method by which we obtain the energy to run our civilization is still by means of the
combustion of fossil fuels. This has two unacceptable effects. The first—and little
realized—is that inhaling gasoline vapors has proved to be carcinogenic to laboratory
animals, and there is an indication that it is one of the causes of the increased spread
of cancer among humans. The second is that the injected into the atmosphere by
combustion is causing global warming.
Electrochemical Technology is involved in a major way in the only alternative to
oil and gasoline as an energy source which also avoids the hazards of nuclear power.
Thus, the collection of solar light and its conversion by means of photovoltaics to
electricity and then the electrochemical splitting of water to yield clean hydrogen,
would provide an inexhaustible replacement for fossil fuels (see Chapter 15). A pilot
plant to do this now exists at Neunburg vorm Wald, in southern Germany.
However, electrochemistry will have to play a broader role than this if sustainable
and clean energy is to become a reality. It provides a general approach that is superior
to conventional chemical approaches for two reasons.