Page 160 - Modern physical chemistry
P. 160
152 Relationships among Reactants
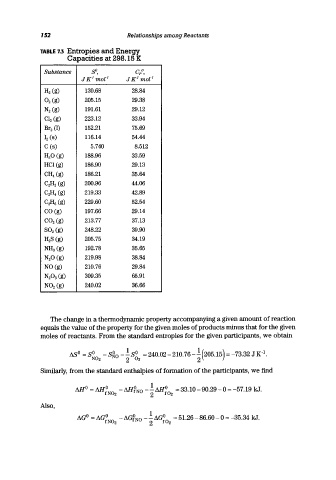
TABLE 7.3 Entropies and Energy
Capacities at 298.15 K
Substance ffi, C/,
J KI moZ- I J KI moZ- I
H2 (g) 130.68 28.84
O2 (g) 205.15 29.38
N2 (g) 191.61 29.12
CI2 (g) 223.12 33.94
Br2 (1) 152.21 75.69
12 (8) 116.14 54.44
C (8) 5.740 8.512
H2 0 (g) 188.96 33.59
HCI (g) 186.90 29.13
CH 4 (g) 186.21 35.64
C2 H2 (g) 200.96 44.06
C2 H 4 (g) 219.33 42.89
C2 H 6 (g) 229.60 52.54
CO (g) 197.66 29.14
CO2 (g) 213.77 37.13
802 (g) 248.22 39.90
H 28 (g) 205.75 34.19
NH3 (g) 192.78 35.65
N2 0 (g) 219.98 38.84
NO (g) 210.76 29.84
N2 0 3 (g) 309.35 65.91
N02 (g) 240.02 36.66
The change in a thennodynamic property accompanying a given amount of reaction
equals the value of the property for the given moles of products minus that for the given
moles of reactants. From the standard entropies for the given participants, we obtain
1
MO = SO -S£o _.!.SOO = 240.02 -210.76-.!.(205.15) = -73.32 J K- •
N02 2 2 2
Similarly, from the standard enthalpies of fonnation of the participants, we find
Also,