Page 155 - Modern physical chemistry
P. 155
7.5 Variation in Heat of Reaction with Thmperature 147
When the pressure on the products is the same as that on the reactants, the heat of
reaction is
[7.18]
Now HB is the enthalpy of the specified amount of products and HA that of the corre-
sponding amount of reactants.
Differentiating the second equality in (7.18) at constant pressure yields
(°:1 =(o~ 1-(°:: 1 =(CP)B-(CP)A =IlC p . [7.19]
In the second step, the energy capacities from formula (4.41) have been introduced. Inte-
grating over temperature gives us the formula
[7.20]
Note that llH2 equals the heat of reaction at T2 and P while llHl equals the heat of reac-
tion at Tl and P following formula (7.18).
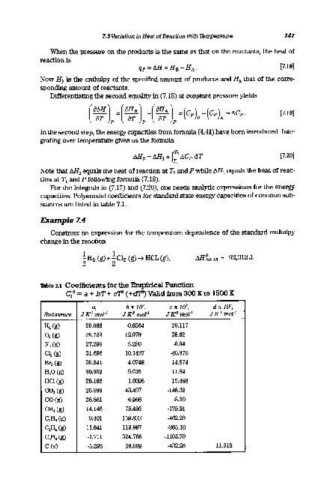
For the integrals in (7.17) and (7.20), one needs analytic expressions for the energy
capacities. Polynomial coefficients for standard state energy capacities of common sub-
stances are listed in table 7.1.
ExampJeZ4
Construct an expression for the temperature dependence of the standard enthalpy
change in the reaction
1 1
-H2 (g)+-CI2 (g)~ HCL (g), llH&S.15 = -92,312 J.
2 2
Table 7.1 Coefficients for the Empirical Function
Cpo =a + bT + cTJ (+d'f3) Valid from 300 K to 1500 K
a, b x 10'1, ex 10 7 , d x 1rfJ,
Substance J Kl mofl J K 2 mofl J K3 mofl JK 4 mof 1
H2 (g) 29.066 -0.8364 20.117
O2 (g) 25.723 12.979 -38.62
N2 (g) 27.296 5.230 -0.04
Cl2 (g) 31.696 10.1437 -40.376
Br2 (g) 35.241 4.0748 -14.874
H2 0 (g) 30.359 9.615 11.84
HCl (g) 28.166 1.8096 15.468
CO2 (g) 25.999 43.497 -148.32
CO (g) 26.861 6.966 -8.20
C~(g) 14.146 75.496 -179.91
C2 Ha (g) 9.401 159.833 -462.29
C2 H 4 (g) 11.841 119.667 -365.10
CaRa (g) -1.711 324.766 -1105.79
C (5) -5.293 58.609 -432.25 11.510