Page 55 - Modular design for machine tools
P. 55
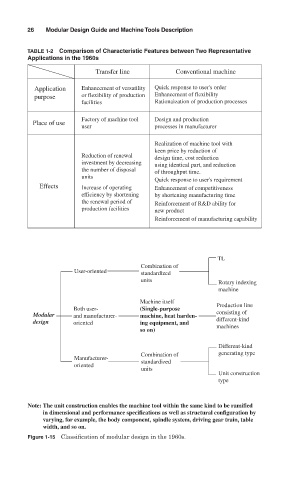
26 Modular Design Guide and Machine Tools Description
TABLE 1-2 Comparison of Characteristic Features between Two Representative
Applications in the 1960s
Transfer line Conventional machine
Application Enhancement of versatility Quick response to user's order
purpose or flexibility of production Enhancement of flexibility
facilities Rationaization of production processes
Factory of machine tool Design and production
Place of use
user processes in manufacturer
Realization of machine tool with
keen price by reduction of
Reduction of renewal design time, cost reduction
investment by decreasing using identical part, and reduction
the number of disposal of throughput time.
units
Quick response to user's requirement
Effects Increase of operating Enhancement of competitiveness
efficiency by shortening by shortening manufacturing time
the renewal period of Reinforcement of R&D ability for
production facilities new product
Reinforcement of manufacturing capability
TL
Combination of
User-oriented standardized
units
Rotary indexing
machine
Machine itself
Both user- (Single-purpose Production line
Modular and manufacturer- machine, heat harden- consisting of
design oriented ing equipment, and different-kind
so on) machines
Different-kind
Combination of generating type
Manufacturer- standardized
oriented
units
Unit construction
type
Note: The unit construction enables the machine tool within the same kind to be ramified
in dimensional and performance specifications as well as structural configuration by
varying, for example, the body component, spindle system, driving gear train, table
width, and so on.
Figure 1-15 Classification of modular design in the 1960s.