Page 23 - Multidimensional Chromatography
P. 23
12 Multidimensional Chromatography
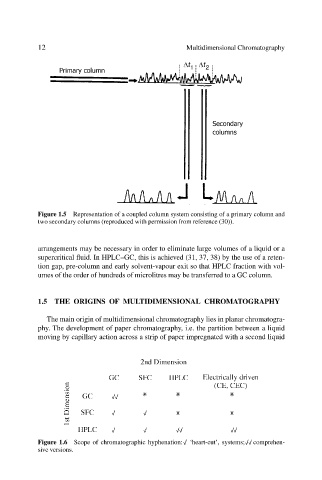
Figure 1.5 Representation of a coupled column system consisting of a primary column and
two secondary columns (reproduced with permission from reference (30)).
arrangements may be necessary in order to eliminate large volumes of a liquid or a
supercritical fluid. In HPLC–GC, this is achieved (31, 37, 38) by the use of a reten-
tion gap, pre-column and early solvent-vapour exit so that HPLC fraction with vol-
umes of the order of hundreds of microlitres may be transferred to a GC column.
1.5 THE ORIGINS OF MULTIDIMENSIONAL CHROMATOGRAPHY
The main origin of multidimensional chromatography lies in planar chromatogra-
phy. The development of paper chromatography, i.e. the partition between a liquid
moving by capillary action across a strip of paper impregnated with a second liquid
Figure 1.6 Scope of chromatographic hyphenation: ‘heart-cut’, systems; comprehen-
sive versions.