Page 160 - Book Hosokawa Nanoparticle Technology Handbook
P. 160
FUNDAMENTALS CH. 3 CHARACTERISTICS AND BEHAVIOR OF NANOPARTICLES AND ITS DISPERSION SYSTEMS
rate in any case. Furthermore, two step sintering has sintering. The liquid phase sintering technique has been
been studied in which a green body is fired at a higher applied not only to such sintering resistant materials but
temperature to obtain higher relative density, followed also to porcelain or refractory. TiC-Ni, ZrC-Ni, WC-Co,
by firing at a lower temperature for a long time to ZnO-Bi O -CoO, AlN-Y O Si N -Y O -Al O SiC-
4
3
3
2
3
2
3,
2
3,
2
restrict grain growth (Fig. 3.5.6) [5]. As a result, a Y O -Al O , are taken for instance of densifiable sys-
2
3
2
3
dense sintered body composed of nano-size grains has tem by liquid phase sintering. Necessary conditions for
been obtained. densification by liquid phase sintering are: (1) enough
Carbides and nitrides have high surface energy but wettability of liquid to solid, (2) some solubility of solid
low self-diffusion constant. Therefore, it is difficult for to liquid, (3) low viscosity of liquid for fast diffusion of
them to be densified by themselves. Such sintering solid through liquid and (4) existence of liquid as much
resistant materials are densified by liquid phase as is sufficient. In the initial stage of liquid phase sin-
tering, grain rearrangement occurs due to capillary
force between particles (Fig. 3.5.7). Sintering rate is
experimentally given by the following equation [6]:
ρ
ll
t 1 y (3.5.38)
a
where l/l is the shrinkage ratio, 1 y is 1.1–1.3. In
2x the middle stage, dissolution–precipitation process is
dominant sintering mechanism to result in densifica-
tion by smoothing of contact interface and dissolution
of finer particles. There are two rate-controlling
processes in liquid phase sintering, diffusion control-
ling process and interfacial reaction controlling
process and they are formulated as the following
ρ dθ’
equations, respectively [7]:
dl
x ⎛ L ⎞ 3 12
DC
⎜ ⎟ t (3.5.39)
⎝ L ⎠ rkT
4
0
dθ
dl’
⎛ L ⎞ 2
Figure 3.5.4 4 K r
C t (3.5.40)
Stress at the neck between two particles. ⎜ ⎝ L ⎠ ⎟ rkT
2
0
Evaporation condensation
Surface diffusion
Volume diffusion
Grain boundary diffusion
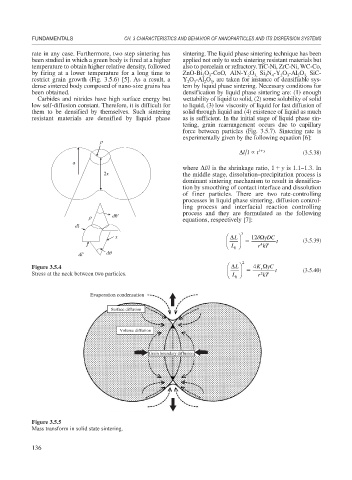
Figure 3.5.5
Mass transform in solid state sintering.
136