Page 164 - Book Hosokawa Nanoparticle Technology Handbook
P. 164
FUNDAMENTALS CH. 3 CHARACTERISTICS AND BEHAVIOR OF NANOPARTICLES AND ITS DISPERSION SYSTEMS
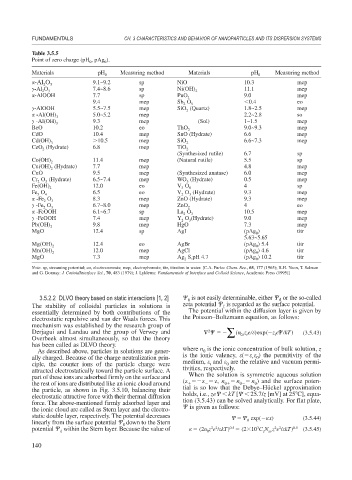
Table 3.5.5
Point of zero charge (pH , pAg ).
0
0
Materials pH 0 Measuring method Materials pH 0 Measuring method
-Al O 9.1~9.2 sp NiO 10.3 mep
2 3
-Al O 3 7.4~8.6 sp Ni(OH) 2 11.1 mep
2
-AlOOH 7.7 sp PuO 2 9.0 mep
9.4 mep Sb O 5 0.4 eo
2
-AlOOH 5.5~7.5 mep SiO (Quartz) 1.8~2.5 mep
2
-Al(OH) 3 5.0~5.2 mep 2.2~2.8 so
-Al(OH) 3 9.3 mep (Sol) 1~1.5 mep
BeO 10.2 eo ThO 2 9.0~9.3 mep
CdO 10.4 mep SnO (Hydrate) 6.6 mep
Cd(OH) 3 10.5 mep SiO 2 6.6~7.3 mep
CeO (Hydrate) 6.8 mep TiO 2
2
(Synthesized rutile) 6.7 sp
Co(OH) 2 11.4 mep (Natural rutile) 5.5 sp
Cu(OH) (Hydrate) 7.7 mep 4.8 mep
2
CuO 9.5 mep (Synthesized anatase) 6.0 mep
Cr O (Hydrate) 6.5~7.4 mep WO (Hydrate) 0.5 mep
3
3
2
Fe(OH) 2 12.0 eo V O 8 4 sp
3
Fe O 4 6.5 eo V O (Hydrate) 9.3 mep
3
3
2
-Fe O 3 8.3 mep ZnO (Hydrate) 9.3 mep
2
-Fe O 3 6.7~8.0 mep ZnO 2 4 eo
2
-FeOOH 6.1~6.7 sp La O 3 10.5 mep
2
-FeOOH 7.4 mep Y O (Hydrate) 9.0 mep
3
2
Pb(OH) 2 9.8 mep HgO 7.3 mep
MgO 12.4 sp AgI (pAg ) titr
0
5.63~5.65
Mg(OH) 2 12.4 eo AgBr (pAg ) 5.4 titr
0
Mn(OH) 2 12.0 mep AgCl (pAg ) 4.6 titr
0
MgO 7.3 mep Ag S,pH 4.7 (pAg ) 10.2 titr
0
2
Note: sp, streaming potential; eo, electroosmosis; mep, electrophoresis; titr, titration in water. [C.A. Parks: Chem. Rev., 65, 177 (1965); R.H. Yoon, T. Salman
and G. Donnay: J. CotioidInterface Sci., 70, 483 (1979); J. Lyklema: Fundamentals of Interface and Colloid Science, Academic Press (1995)]
3.5.2.2 DLVO theory based on static interactions [1, 2] is not easily determinable, either d or the so-called
0
The stability of colloidal particles in solutions is zeta potential is regarded as the surface potential.
essentially determined by both contributions of the The potential within the diffusion layer is given by
electrostatic repulsive and van der Waals forces. This the Poisson–Boltzmann equation, as follows:
mechanism was established by the research group of
Derjagui and Landau and the group of Verwey and ∑ (nz e )exp( z e kT ) (3.5.43)
2
i
0ii
Overbeek almost simultaneously, so that the theory
has been called as DLVO theory.
As described above, particles in solutions are gener- where n is the ionic concentration of bulk solution, z
0
ally charged. Because of the charge neutralization prin- is the ionic valency, ( ) the permitivity of the
r 0
ciple, the counter ions of the particle charge were medium, and are the relative and vacuum permi-
0
r
attracted electrostatically toward the particle surface. A tivities, respectively.
part of these ions are adsorbed firmly on the surface and When the solution is symmetric aqueous solution
the rest of ions are distributed like an ionic cloud around (z z z, n n n ) and the surface poten-
0
0
0
the particle, as shown in Fig. 3.5.10, balancing their tial is so low that the Debye–Hückel approximation
electrostatic attractive force with their thermal diffusion holds, i.e., ze kT [ 25.7/z [mV] at 25 C], equa-
force. The above-mentioned firmly adsorbed layer and tion (3.5.43) can be solved analytically. For flat plate,
the ionic cloud are called as Stern layer and the electro- is given as follows:
static double layer, respectively. The potential decreases exp( x) (3.5.44)
linearly from the surface potential down to the Stern 0
0
potential within the Stern layer. Because the value of (2n z e / kT) (2 10 C N z e / kT) 0.5 (3.5.45)
3
2 2
0.5
2 2
d 0 e av
140