Page 169 - Book Hosokawa Nanoparticle Technology Handbook
P. 169
3.5 INTERACTIONS BETWEEN PARTICLES FUNDAMENTALS
The roles of polymer flocculants have been esti- surfaces of the small separation distance, say 10 nm,
mated by the results of macroscopic experiments, but become extremely unstable because of the poor affin-
sometimes the estimated mechanism differs from the ity of water molecules to the surface. This phenome-
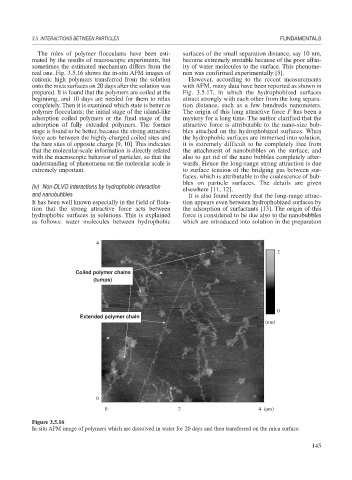
real one. Fig. 3.5.16 shows the in-situ AFM images of non was confirmed experimentally [5].
cationic high polymers transferred from the solution However, according to the recent measurements
onto the mica surfaces on 20 days after the solution was with AFM, many data have been reported as shown in
prepared. It is found that the polymers are coiled at the Fig. 3.5.17, in which the hydrophobized surfaces
beginning, and 10 days are needed for them to relax attract strongly with each other from the long separa-
completely. Then it is examined which state is better as tion distance, such as a few hundreds nanometers.
polymer flocculants; the initial stage of the island-like The origin of this long attractive force F has been a
adsorption coiled polymers or the final stage of the mystery for a long time. The author clarified that the
adsorption of fully extended polymers. The former attractive force is attributable to the nano-size bub-
stage is found to be better, because the strong attractive bles attached on the hydrophobized surfaces. When
force acts between the highly-charged coiled sites and the hydrophobic surfaces are immersed into solution,
the bare sites of opposite charge [9, 10]. This indicates it is extremely difficult to be completely free from
that the molecular-scale information is directly related the attachment of nanobubbles on the surface, and
with the macroscopic behavior of particles, so that the also to get rid of the nano bubbles completely after-
understanding of phenomena on the molecular scale is wards. Hence the long-range strong attraction is due
extremely important. to surface tension of the bridging gas between sur-
faces, which is attributable to the coalescence of bub-
bles on particle surfaces. The details are given
(iv) Non-DLVO interactions by hydrophobic interaction
elsewhere [11, 12].
and nanobubbles It is also found recently that the long-range attrac-
It has been well known especially in the field of flota- tion appears even between hydrophobized surfaces by
tion that the strong attractive force acts between the adsorption of surfactants [13]. The origin of this
hydrophobic surfaces in solutions. This is explained force is considered to be due also to the nanobubbles
as follows: water molecules between hydrophobic which are introduced into solution in the preparation
4
2
Coiled polymer chains
(lumps)
0
Extended polymer chain
(nm)
0
0 2 4 (µm)
Figure 3.5.16
In-situ AFM image of polymers which are dissolved in water for 20 days and then transferred on the mica surface.
145