Page 171 - Book Hosokawa Nanoparticle Technology Handbook
P. 171
3.5 INTERACTIONS BETWEEN PARTICLES FUNDAMENTALS
should be able to thoroughly understand only after for the present nanometer scale measurement, became
measuring them directly and precisely. possible by introducing fringes of equal chromatic
order (FECO) interferometry developed by Tabor et
(1) Surface forces measurement al. [3]. The DLVO theory for discussing the stability
(a) Surface forces of colloidal dispersions was proved in the late 1970s,
when a prototype of the present surface forces appa-
The surface forces are proportional to the surface area
involved. Frictional and adhesion forces are also a ratus (SFA) was completed for the measurements of
part of the surface forces. Typical surface forces are surface interactions in liquids [4].
van der Waals force, electrical double-layer force The surface force apparatus as well as the colloidal
between charged surfaces, steric forces due to the size probe atomic force microscopy [5] are employed for
and shape of molecules, and the solvation force. The surface force measurements. When we use the former
first two forces, i.e. van der Waals force and electrical instrument, the resolutions of distance and force are
double-layer force, are called the DLVO force, and 0.1 nm and 1 nN, respectively. The geometry of the
other forces are often classified as the non-DLVO sample surfaces is in two crossed cylinders for the
force (see Sections 3.5.1 and 3.5.2). former, and a sphere and a flat plate for the latter.
From the early stage of this research, these geometries
(b) Surface forces measurement have been adopted to avoid the complicated adjust-
ment such as keeping two flat surfaces parallel. It is
This method directly measures the distance depend-
ence of interaction (interaction potential) between known that the measured surface force (F) normal-
surfaces using a spring balance. It provides the ized by the radius of the surface curvature (R) is pro-
knowledge about the distance dependence and magni- portional to the interaction energy between flat
tude of the surface forces. It is also possible to calcu- surfaces (G ) (F/R 2 G : Derjagnin approxima-
f
f
late the force, adhesive force, necessary for separating tion), therefore, this geometry is also convenient for
the surfaces in the adhesive contact [1]. comparing the experimental results with the theory.
Surface force measurement was first developed to
realize the dispersion forces. The initial attempt of (c) Measurement method [6]
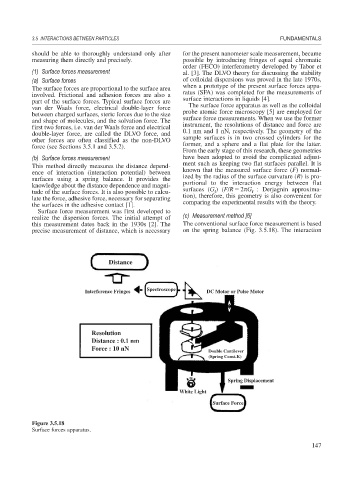
this measurement dates back in the 1930s [2]. The The conventional surface force measurement is based
precise measurement of distance, which is necessary on the spring balance (Fig. 3.5.18). The interaction
Distance
Spectroscope
Interference Fringes DC Motor or Pulse Motor
Resolution
Distance : 0.1 nm
Force : 10 nN
Double Cantilever
(Spring Const.K)
Spring Displacement
White Light
Surface Force
Figure 3.5.18
Surface forces apparatus.
147