Page 207 - Book Hosokawa Nanoparticle Technology Handbook
P. 207
4.2 NANOPARTICLES ARRANGED STRUCTURES FUNDAMENTALS
biomineralization and the mild synthesis condition, “at Phage display method is a combinatorial chem-
room temperature in neutral solution”, attracts immense istry, in which a molecule with desired function is
interest in the hybridization with heat-labile or pH- selected by screening from a great diversity of
sensitive organic compounds. Here, we show you recent molecular population called library. The problems
biomineralization studies by combinatorial procedure. for the combinatorial library approach are how to
make library, how to screen desired molecule, and
how to analyze the selected low-concentrated mole-
4.2.2.1 Functional biomolecules: Peptide and protein
cule. In the case that peptide/protein is an element in
In general, peptide and protein play an important role library, the use of a kind of virus, phage, can solve
on biomineralization, as a framework and catalyst. the problems.
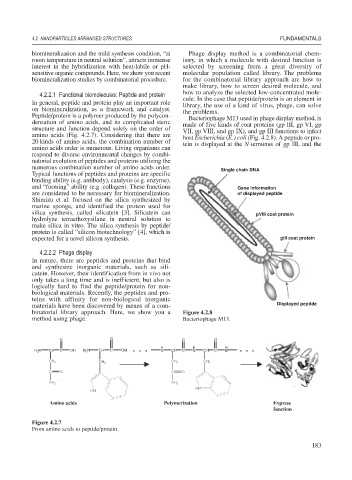
Peptide/protein is a polymer produced by the polycon- Bacteriophage M13 used in phage display method, is
densation of amino acids, and its complicated steric made of five kinds of coat proteins (gp III, gp VI, gp
structure and function depend solely on the order of VII, gp VIII, and gp IX), and gp III functions to infect
amino acids (Fig. 4.2.7). Considering that there are host Escherichia (E.) coli (Fig. 4.2.8). A peptide or pro-
20 kinds of amino acids, the combination number of tein is displayed at the N-terminus of gp III, and the
amino acids order is numerous. Living organisms can
respond to diverse environmental changes by combi-
natorial evolution of peptides and proteins utilizing the
numerous combination number of amino acids order. Single chain DNA
Typical functions of peptides and proteins are specific
binding ability (e.g. antibody), catalysis (e.g. enzyme),
and “forming” ability (e.g. collagen). These functions Gene information
are considered to be necessary for biomineralization. of displayed peptide
Shimizu et al. focused on the silica synthesized by
marine sponge, and identified the protein used for
silica synthesis, called silicatein [3]. Silicatein can pVIII coat protein
hydrolyze tetraethoxysilane in neutral solution to
make silica in vitro. The silica synthesis by peptide/
protein is called “silicon biotechnology” [4], which is
expected for a novel silicon synthesis. gIII coat protein
4.2.2.2 Phage display
In nature, there are peptides and proteins that bind
and synthesize inorganic materials, such as sili-
catein. However, their identification from in vivo not
only takes a long time and is inefficient, but also is
logically hard to find the peptide/protein for non-
biological materials. Recently, the peptides and pro-
teins with affinity for non-biological inorganic
materials have been discovered by means of a com- Displayed peptide
binatorial library approach. Here, we show you a Figure 4.2.8
method using phage. Bacteriophage M13.
O O O O
H H H
H 2 N CH C OH H 2 N CH C OH • • • N CH C N CH C N • • •
CH 2 CH 2 CH 2 CH 2
C O C O
NH 2 NH 2
HN
HN
Amino acids Polymerization Express
function
Figure 4.2.7
From amino acids to peptide/protein.
183