Page 208 - Book Hosokawa Nanoparticle Technology Handbook
P. 208
FUNDAMENTALS CH. 4 CONTROL OF NANOSTRUCTURE OF MATERIALS
Mixing with inorganic particles
Displayed Separation
peptide
Infection
Peptide library
displayed on phages
DNA identification
Amplification
of phage
Amino acid sequence
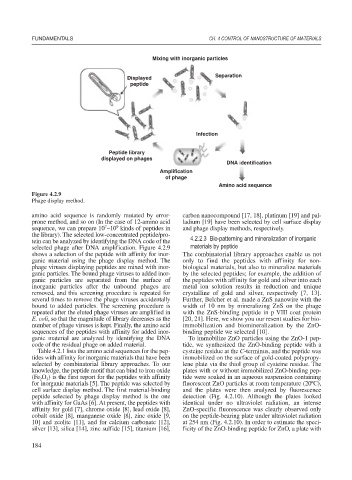
Figure 4.2.9
Phage display method.
amino acid sequence is randomly mutated by error- carbon nanocompound [17, 18], platinum [19] and pal-
prone method, and so on (In the case of 12-amino acid ladium [19] have been selected by cell surface display
7
9
sequence, we can prepare 10 ~10 kinds of peptides in and phage display methods, respectively.
the library). The selected low-concentrated peptide/pro-
tein can be analyzed by identifying the DNA code of the 4.2.2.3 Bio-patterning and mineralization of inorganic
selected phage after DNA amplification. Figure 4.2.9 materials by peptide
shows a selection of the peptide with affinity for inor- The combinatorial library approaches enable us not
ganic material using the phage display method. The only to find the peptides with affinity for non-
phage viruses displaying peptides are mixed with inor- biological materials, but also to mineralize materials
ganic particles. The bound phage viruses to added inor- by the selected peptides; for example, the addition of
ganic particles are separated from the surface of the peptides with affinity for gold and silver into each
inorganic particles after the unbound phages are metal ion solution results in reduction and unique
removed, and this screening procedure is repeated for crystalline of gold and silver, respectively [7, 13].
several times to remove the phage viruses accidentally Further, Belcher et al. made a ZnS nanowire with the
bound to added particles. The screening procedure is width of 10 nm by mineralizing ZnS on the phage
repeated after the eluted phage viruses are amplified in with the ZnS-binding peptide in p VIII coat protein
E. coli, so that the magnitude of library decreases as the [20, 21]. Here, we show you our resent studies for bio-
number of phage viruses is kept. Finally, the amino acid immobilization and biomineralization by the ZnO-
sequences of the peptides with affinity for added inor- binding peptide we selected [10].
ganic material are analyzed by identifying the DNA To immobilize ZnO particles using the ZnO-1 pep-
code of the residual phage on added material. tide, we synthesized the ZnO-binding peptide with a
Table 4.2.1 lists the amino acid sequences for the pep- cysteine residue at the C-terminus, and the peptide was
tides with affinity for inorganic materials that have been immobilized on the surface of gold-coated polypropy-
selected by combinatorial library approaches. To our lene plate via the thiol group of cysteine residue. The
knowledge, the peptide motif that can bind to iron oxide plates with or without immobilized ZnO-binding pep-
(Fe O ) is the first report for the peptides with affinity tide were soaked in an aqueous suspension containing
2
3
for inorganic materials [5]. The peptide was selected by fluorescent ZnO particles at room temperature (20ºC),
cell surface display method. The first material-binding and the plates were then analyzed by fluorescence
peptide selected by phage display method is the one detection (Fig. 4.2.10). Although the plates looked
with affinity for GaAs [6]. At present, the peptides with identical under no ultraviolet radiation, an intense
affinity for gold [7], chrome oxide [8], lead oxide [8], ZnO-specific fluorescence was clearly observed only
cobalt oxide [8], manganese oxide [8], zinc oxide [9, on the peptide-bearing plate under ultraviolet radiation
10] and zeolite [11], and for calcium carbonate [12], at 254 nm (Fig. 4.2.10). In order to estimate the speci-
silver [13], silica [14], zinc sulfide [15], titanium [16], ficity of the ZnO-binding peptide for ZnO, a plate with
184