Page 288 - Book Hosokawa Nanoparticle Technology Handbook
P. 288
4.6 SELF-ASSEMBLY FUNDAMENTALS
(a) violegen [17], and cyclic amine compounds [18].
Adsorption analysis clearly indicates that the
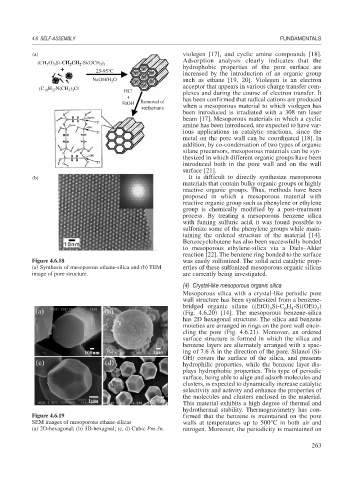
(CH 3 O) 3 Si-CH 2 CH 2 -Si(OCH 3 ) 3
hydrophobic properties of the pore surface are
25-95°C
increased by the introduction of an organic group
NaOH/H O such as ethane [19, 20]. Violegen is an electron
2
acceptor that appears in various charge transfer com-
(C 18 H 37 N(CH 3 ) 3 Cl
HCl plexes and during the course of electron transfer. It
+ has been confirmed that radical cations are produced
EtOH Removal of
surfactants when a mesoporous material to which violegen has
been introduced is irradiated with a 308 nm laser
beam [17]. Mesoporous materials in which a cyclic
amine has been introduced, are expected to have var-
ious applications in catalytic reactions, since the
metal on the pore wall can be coordinated [18]. In
addition, by co-condensation of two types of organic
silane precursors, mesoporous materials can be syn-
thesized in which different organic groups have been
introduced both in the pore wall and on the wall
surface [21].
(b) It is difficult to directly synthesize mesoporous
materials that contain bulky organic groups or highly
reactive organic groups. Thus, methods have been
proposed in which a mesoporous material with
reactive organic group such as phenylene or ethylene
group is chemically modified by a post-treatment
process. By treating a mesoporous benzene silica
with fuming sulfuric acid, it was found possible to
sulfonize some of the phenylene groups while main-
taining the ordered structure of the material [14].
Benzocyclobutene has also been successfully bonded
to mesoporous ethylene-silica via a Diels–Alder
reaction [22]. The benzene ring bonded to the surface
Figure 4.6.18 was easily sulfonized. The solid acid catalytic prop-
(a) Synthesis of mesoporous ethane-silica and (b) TEM erties of these sulfonized mesoporous organic silicas
image of pore structure. are currently being investigated.
(4) Crystal-like mesoporous organic silica
Mesoporous silica with a crystal-like periodic pore
wall structure has been synthesized from a benzene-
bridged organic silane ((EtO) Si-C H -Si(OEt) )
3
4
3
6
(Fig. 4.6.20) [14]. The mesoporous benzene-silica
has 2D hexagonal structure. The silica and benzene
moieties are arranged in rings on the pore wall encir-
cling the pore (Fig. 4.6.21). Moreover, an ordered
surface structure is formed in which the silica and
benzene layers are alternately arranged with a spac-
ing of 7.6 Å in the direction of the pore. Silanol (Si-
OH) covers the surface of the silica, and presents
hydrophilic properties, while the benzene layer dis-
plays hydrophobic properties. This type of periodic
surface, being able to align and adsorb molecules and
clusters, is expected to dynamically increase catalytic
selectivity and activity and enhance the properties of
the molecules and clusters enclosed in the material.
This material exhibits a high degree of thermal and
hydrothermal stability. Thermogravimetry has con-
Figure 4.6.19 firmed that the benzene is maintained on the pore
SEM images of mesoporous ethane-silicas walls at temperatures up to 500°C in both air and
(a) 2D-hexagonal; (b) 3D-hexagnal; (c, d) Cubic Pm-3n. nitrogen. Moreover, the periodicity is maintained on
263