Page 402 - Book Hosokawa Nanoparticle Technology Handbook
P. 402
FUNDAMENTALS CH. 6 EVALUATION METHODS FOR PROPERTIES OF NANOSTRUCTURED BODY
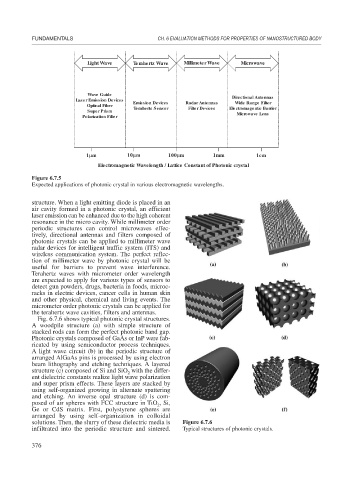
Light Wave Terahertz Wave Millimeter Wave Microwave
Wave Guide
Laser Emission Devices Directional Antennas
Emission Devices Radar Antennas Wide Range Filter
Optical Fiber Teraherts Sensor Filter Devices Electromagentic Barrier
Super Prism
Microwave Lens
Polarization Filter
1μm 10μm 100μm 1mm 1cm
Electromagnetic Wavelength / Lattice Constant of Photonic crystal
Figure 6.7.5
Expected applications of photonic crystal in various electromagnetic wavelengths.
structure. When a light emitting diode is placed in an
air cavity formed in a photonic crystal, an efficient
laser emission can be enhanced due to the high coherent
resonance in the micro cavity. While millimeter order
periodic structures can control microwaves effec-
tively, directional antennas and filters composed of
photonic crystals can be applied to millimeter wave
radar devices for intelligent traffic system (ITS) and
wireless communication system. The perfect reflec-
tion of millimeter wave by photonic crystal will be
useful for barriers to prevent wave interference.
Terahertz waves with micrometer order wavelength
are expected to apply for various types of sensors to
detect gun powders, drugs, bacteria in foods, microc-
racks in electric devices, cancer cells in human skin
and other physical, chemical and living events. The
micrometer order photonic crystals can be applied for
the terahertz wave cavities, filters and antennas.
Fig. 6.7.6 shows typical photonic crystal structures.
A woodpile structure (a) with simple structure of
stacked rods can form the perfect photonic band gap.
Photonic crystals composed of GaAs or InP were fab-
ricated by using semiconductor process techniques.
A light wave circuit (b) in the periodic structure of
arranged AlGaAs pins is processed by using electron
beam lithography and etching techniques. A layered
structure (c) composed of Si and SiO with the differ-
2
ent dielectric constants realize light wave polarization
and super prism effects. These layers are stacked by
using self-organized growing in alternate spattering
and etching. An inverse opal structure (d) is com-
posed of air spheres with FCC structure in TiO , Si,
2
Ge or CdS matrix. First, polystyrene spheres are
arranged by using self-organization in colloidal
solutions. Then, the slurry of these dielectric media is Figure 6.7.6
infiltrated into the periodic structure and sintered. Typical structures of photonic crystals.
376