Page 450 - Book Hosokawa Nanoparticle Technology Handbook
P. 450
APPLICATIONS 1 DISPERSION OF FINE SILICA PARTICLES
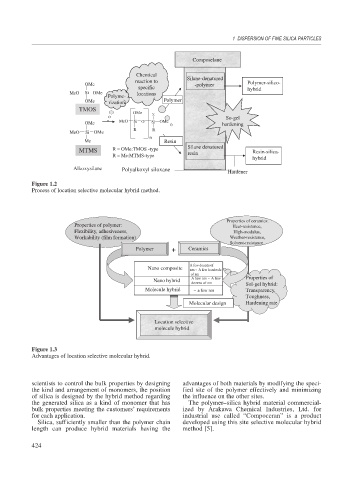
Composelane
Chemical
reaction to Silane-denatured Polymer-silico-
OMe -polymer
specific hybrid
MeO Si OMe locations
Polyme-
OMe rization Polymer
TMOS
OMe
X
So-gel
OMe MeO Si O Si OMe hardening
R R
MeO Si OMe
n
Me Resin
Silane denatured
MTMS R = OMe:TMOS -type Resin-silica-
R = Me:MTMS-type resin
hybrid
Alkoxysilane Polyalkoxyl siloxane Hardener
Figure 1.2
Process of location selective molecular hybrid method.
Properties of ceramics:
Properties of polymer: Heat-resistance,
Flexibility, adhesiveness, High-modulus,
Workability (film formation) Weather-resistance,
Solvent-resistance
Polymer
ƒŠ
ƒ}
•[
ƒ|ƒŠƒ}•[ + + Ceramics
ƒ|
A few dozens of
Nano composite nm ~ A few hundreds
of nm
A few nm ~ A few Properties of
Nano hybrid
dozens of nm Sol-gel hybrid:
Molecule hybrid ~ a few nm Transparency,
Toughness,
Molecular design Hardening rate
Location selective
molecule hybrid
Figure 1.3
Advantages of location selective molecular hybrid.
scientists to control the bulk properties by designing advantages of both materials by modifying the speci-
the kind and arrangement of monomers, the position fied site of the polymer effectively and minimizing
of silica is designed by the hybrid method regarding the influence on the other sites.
the generated silica as a kind of monomer that has The polymer–silica hybrid material commercial-
bulk properties meeting the customers’ requirements ized by Arakawa Chemical Industries, Ltd. for
for each application. industrial use called “Compoceran” is a product
Silica, sufficiently smaller than the polymer chain developed using this site selective molecular hybrid
length can produce hybrid materials having the method [5].
424