Page 451 - Book Hosokawa Nanoparticle Technology Handbook
P. 451
1 DISPERSION OF FINE SILICA PARTICLES APPLICATIONS
3. Unmeltable plastics: epoxy resin hybrid substrates of silica, this hybrid material is utilized as a
base material for various industrial applications. As for
The properties of polymer materials are heavily deteri- the electrical insulation material related with the printed
orated when the temperature exceeds Tg (glass transi- board, its high heat-resistance and good electrical insu-
tion temperature) and is softened. In addition, there is lating property are highly evaluated and used for resist
increasing need for heat-resistant and flame-retarded ink, electric resistant resin between the build-up board
epoxy resins in advanced fields such as the electronic layers and reinforcing materials.
device industry as halogenated epoxy resin may For semiconductors, this hybrid material is being
become unusable because of environmental issues. used as a heat-resisting component for anisotropic
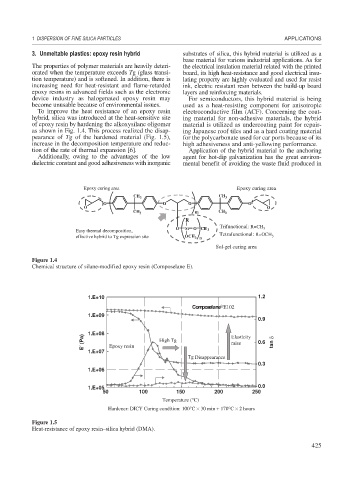
To improve the heat resistance of an epoxy resin electroconductive film (ACF). Concerning the coat-
hybrid, silica was introduced at the heat-sensitive site ing material for non-adhesive materials, the hybrid
of epoxy resin by hardening the alkoxysilane oligomer material is utilized as undercoating paint for repair-
as shown in Fig. 1.4. This process realized the disap- ing Japanese roof tiles and as a hard coating material
pearance of Tg of the hardened material (Fig. 1.5), for the polycarbonate used for car ports because of its
increase in the decomposition temperature and reduc- high adhesiveness and anti-yellowing performance.
tion of the rate of thermal expansion [6]. Application of the hybrid material to the anchoring
Additionally, owing to the advantages of the low agent for hot-dip galvanization has the great environ-
dielectric constant and good adhesiveness with inorganic mental benefit of avoiding the waste fluid produced in
Epoxy curing area Epoxy curing area
CH CH
3 3
O O O O O O
O O
CH m m CH
3 3
R
Trifunctional: R=CH
O Si O CH 3
Easy thermal decomposition, O CH 3 3
Tetrafunctional: R=OCH
effective hybrid to Tg expression site OCH 3 n 3
Sol-gel curing area
Figure 1.4
Chemical structure of silane-modified epoxy resin (Composelane E).
1.E+10 1.2
Composelane ® E102
1.E+09
0.9
1.E+08 Elasticity
E′ (Pa) Epoxy resin High Tg raise 0.6 tan δ δ
1.E+07
Tg Disappearance
0.3
1.E+06
1.E+05 0.0
50 100 150 200 250
Temperature (°C)
Hardener: DICY Curing condition: 100°C × 30 min + 170°C × 2 hours
Figure 1.5
Heat-resistance of epoxy resin–silica hybrid (DMA).
425