Page 455 - Book Hosokawa Nanoparticle Technology Handbook
P. 455
2 GENERATION OF METAL NANOPARTICLES APPLICATIONS
Table 2.1
The example of manufacturing nanoparticles.
Material Atmosphere Obtained
gas kind particles
Pure metal Hydrogen Fe, Cu, Ni, Co,
Cr, Ti, In, ...
Alloy Hydrogen Fe–Ni, Fe–Co,
Ag–Cu, Ag–Pd, ...
Metal or nitride Nitrogen TiN, ZrN,
AlN, AlN Al, ...
Metal or carbide Hydrogen SiC, TiC, ...
Boronide Hydrogen LaB 6
Metal or oxide Oxygen WO , MoO ,
3
3
Nb O , ...
2
5
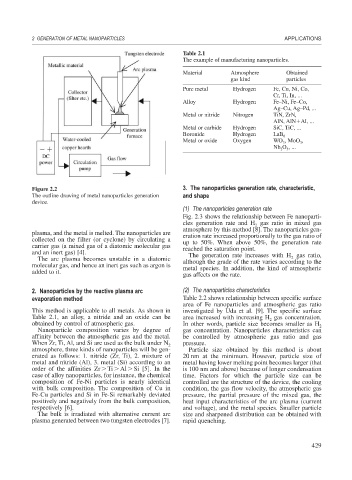
Figure 2.2 3. The nanoparticles generation rate, characteristic,
The outline drawing of metal nanoparticles generation and shape
device.
(1) The nanoparticles generation rate
Fig. 2.3 shows the relationship between Fe nanoparti-
cles generation rate and H gas ratio in mixed gas
2
atmosphere by this method [8]. The nanoparticles gen-
plasma, and the metal is melted. The nanoparticles are eration rate increased proportionally to the gas ratio of
collected on the filter (or cyclone) by circulating a up to 50%. When above 50%, the generation rate
carrier gas (a mixed gas of a diatomic molecular gas reached the saturation point.
and an inert gas) [4]. The generation rate increases with H gas ratio,
2
The arc plasma becomes unstable in a diatomic although the grade of the rate varies according to the
molecular gas, and hence an inert gas such as argon is metal species. In addition, the kind of atmospheric
added to it.
gas affects on the rate.
2. Nanoparticles by the reactive plasma arc (2) The nanoparticles characteristics
evaporation method Table 2.2 shows relationship between specific surface
area of Fe nanoparticles and atmospheric gas ratio
This method is applicable to all metals. As shown in investigated by Uda et al. [9]. The specific surface
Table 2.1, an alloy, a nitride and an oxide can be area increased with increasing H gas concentration.
2
obtained by control of atmospheric gas. In other words, particle size becomes smaller as H 2
Nanoparticle composition varies by degree of gas concentration. Nanoparticles characteristics can
affinity between the atmospheric gas and the metal. be controlled by atmospheric gas ratio and gas
When Zr, Ti, Al, and Si are used as the bulk under N 2 pressure.
atmosphere, three kinds of nanoparticles will be gen- Particle size obtained by this method is about
erated as follows: 1. nitride (Zr, Ti), 2. mixture of 20 nm at the minimum. However, particle size of
metal and nitride (Al), 3. metal (Si) according to an metal having lower melting point becomes larger (that
order of the affinities Zr Ti Al Si [5]. In the is 100 nm and above) because of longer condensation
case of alloy nanoparticles, for instance, the chemical time. Factors for which the particle size can be
composition of Fe-Ni particles is nearly identical controlled are the structure of the device, the cooling
with bulk composition. The composition of Cu in condition, the gas flow velocity, the atmospheric gas
Fe-Cu particles and Si in Fe-Si remarkably deviated pressure, the partial pressure of the mixed gas, the
positively and negatively from the bulk composition, heat input characteristics of the arc plasma (current
respectively [6]. and voltage), and the metal species. Smaller particle
The bulk is irradiated with alternative current arc size and sharpened distribution can be obtained with
plasma generated between two tungsten electrodes [7]. rapid quenching.
429