Page 473 - Book Hosokawa Nanoparticle Technology Handbook
P. 473
APPLICATIONS 6 DESIGN OF NANOPARTICLES FOR ORAL DELIVERY OF PEPTIDE DRUGS
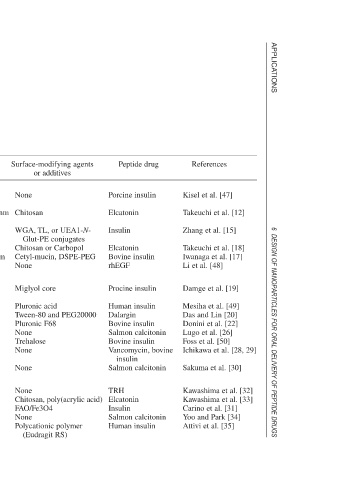
References Kisel et al. [47] Takeuchi et al. [12] Zhang et al. [15] Takeuchi et al. [18] Iwanaga et al. [17] Li et al. [48] Damge et al. [19] Mesiha et al. [49] Das and Lin [20] Donini et al. [22] Lugo et al. [26] Foss et al. [50] Ichikawa et al. [28, 29] Sakuma et al. [30] Kawashima et al. [32] Kawashima et al. [33] Carino et al. [31] Y oo and Park [34] Attivi et al. [35]
Peptide drug Porcine insulin Elcatonin Insulin Elcatonin Bovine insulin rhEGF Procine insulin Human insulin Dalargin Bovine insulin Salmon calcitonin Bovine insulin Vancomycin, bovine insulin Salmon calcitonin TRH Elcatonin Insulin Salmon calcitonin Human insulin
Surface-modifying agents or additives None Chitosan WGA, TL, or UEA1-N- Glut-PE conjugates Chitosan or Carbopol Cetyl-mucin, DSPE-PEG None Miglyol core Pluronic acid Tween-80 and PEG20000 Pluronic F68 None Trehalose None None None Chitosan, poly(acrylic acid) FAO/Fe3O4 None Polycationic polymer (Eudragit RS)
Characteristics of representative nanoparticulate carriers for oral peptide delivery.
Particle size 50–250 nm 470, 660, 4100 nm 190 nm N/A 348, 453, 479 nm 306 nm 220 nm 85 nm 100 nm 300 nm 200–1200 nm 230–340 nm 170–350 nm 400–1250 nm 250 nm 240 nm 1 m (80%) 171–315 nm 350 nm
Preparation method Thin-layer hydration/ ultrasonication Thin-layer hydration/ ultrasonication Reverse evaporation Thin-layer hydration Thin-layer hydration Thin-layer hydration Interfacial emulsion polymerization In situ ionic polymerization Ionic polymerization Dispersion polymerization Dispersion polymerization Dispersion polymerization Dispersion polymerization Dispersion polymerization Emulsion-solvent diffusion Emulsion-solvent diffusion Phase inversion Solvent diffusion Multiple emulsion evaporation
Carrier type and base materials Phosphatidylethanol based lipids DPPC/DCP or SA DPPC/Chol/DOPE-PEG Poly(alkyl(meth)acrylates) P(NIPAAm)/P(MAA-g-EG) P(St)/hydrophilic polymer chains Polyesters/polyanhydrides
Table 6.1 Liposomes DSPC/DCP/Chol Soyalecithin/Chol DPPC/Chol/SA P(IBCN) P(IBCN) P(IBCN) P(MAA-g-EG) P(MAA-g-EG) P(AA-g-EG) PLGA PLGA PLGA PLGA PCL
446