Page 470 - Book Hosokawa Nanoparticle Technology Handbook
P. 470
APPLICATIONS 6 DESIGN OF NANOPARTICLES FOR ORAL DELIVERY OF PEPTIDE DRUGS
Base materials
Nano-
particle Drug
Drug
Drug-loaded Drug-loading
nano-carriers • Retainable drug-stability
• High loading efficiency, high drug content
Digestive enzymes
H +
H + H +
H + H +
In the stomach
• Protection against enzymatic degradation
H + • Prevention of drug-leaching
Digestive enzymes • Good redispersibility of nano-carriers
H + Digestive enzymes
Nano-carriers
Mucus layer
Absorptive enterocytes (EC)
M cell (MC)
TJ
Tight junction (TJ)
MC EC
In the small intestine
• Timing and mode of drug release
• Redispersibility
• Muco-adhesiveness / muco-penetrability
Lymphoid tissue (lymphocytes, macrophages) • Translocation routes for drug and nano-carriers
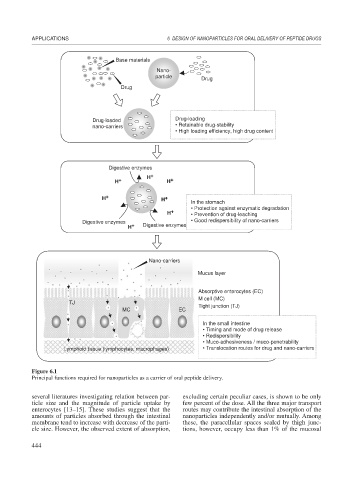
Figure 6.1
Principal functions required for nanoparticles as a carrier of oral peptide delivery.
several literatures investigating relation between par- excluding certain peculiar cases, is shown to be only
ticle size and the magnitude of particle uptake by few percent of the dose. All the three major transport
enterocytes [13–15]. These studies suggest that the routes may contribute the intestinal absorption of the
amounts of particles absorbed through the intestinal nanoparticles independently and/or mutually. Among
membrane tend to increase with decrease of the parti- these, the paracellular spaces sealed by thigh junc-
cle size. However, the observed extent of absorption, tions, however, occupy less than 1% of the mucosal
444