Page 467 - Book Hosokawa Nanoparticle Technology Handbook
P. 467
5 A DYE-SENSITIZED SOLAR CELL UTILIZING METAL NANOPARTICLE APPLICATIONS
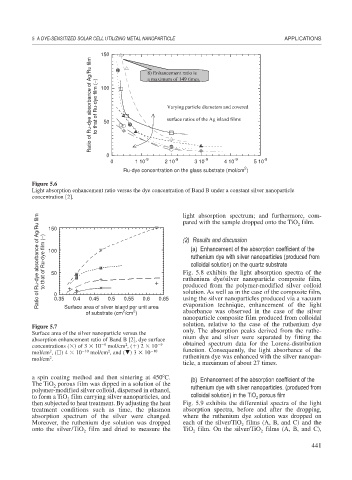
150 8) Enhancement ratio is
Ratio of Ru-dye absorbance of Ag/Ru film to that of Ru-dye film (−) 100 Varying particle diameters and covered
a maximum of 149 times.
surface ratios of the Ag island films
50
0
-9 -9 -9 -9 -9
0 1 10 2 10 3 10 4 10 5 10
2
Ru-dye concentration on the glass substrate (mol/cm )
Figure 5.6
Light absorption enhancement ratio versus the dye concentration of Band B under a constant silver nanoparticle
concentration [2]. light absorption spectrum; and furthermore, com-
Ratio of Ru-dye absorbance of Ag/Ru film to that of Ru-dye film (−) 100 (2) Results and discussion
pared with the sample dropped onto the TiO film.
2
150
(a) Enhancement of the absorption coefficient of the
ruthenium dye with silver nanoparticles (produced from
colloidal solution) on the quartz substrate
Fig. 5.8 exhibits the light absorption spectra of the
50
ruthenium dye/silver nanoparticle composite film,
produced from the polymer-modified silver colloid
0
using the silver nanoparticles produced via a vacuum
0.45
0.55
0.5
0.4
0.35
evaporation technique, enhancement of the light
Surface area of silver island per unit area
absorbance was observed in the case of the silver
2
2
of substrate (cm /cm ) 0.6 0.65 solution. As well as in the case of the composite film,
nanoparticle composite film produced from colloidal
solution, relative to the case of the ruthenium dye
Figure 5.7
Surface area of the silver nanoparticle versus the only. The absorption peaks derived from the ruthe-
absorption enhancement ratio of Band B [2], dye surface nium dye and silver were separated by fitting the
2
concentrations ( ) of 3 10 9 mol/cm , ( ) 2 10 9 obtained spectrum data for the Lorenz-distribution
2
2
mol/cm , ( ) 4 10 10 mol/cm , and ( ) 3 10 10 function. Consequently, the light absorbance of the
2
mol/cm . ruthenium dye was enhanced with the silver nanopar-
ticle, a maximum of about 27 times.
a spin coating method and then sintering at 450 C. (b) Enhancement of the absorption coefficient of the
The TiO porous film was dipped in a solution of the ruthenium dye with silver nanoparticles. (produced from
2
polymer-modified silver colloid, dispersed in ethanol,
to form a TiO film carrying silver nanoparticles, and colloidal solution) in the TiO porous film
2
2
then subjected to heat treatment. By adjusting the heat Fig. 5.9 exhibits the differential spectra of the light
treatment conditions such as time, the plasmon absorption spectra, before and after the dropping,
absorption spectrum of the silver were changed. where the ruthenium dye solution was dropped on
Moreover, the ruthenium dye solution was dropped each of the silver/TiO films (A, B, and C) and the
2
onto the silver/TiO film and dried to measure the TiO film. On the silver/TiO films (A, B, and C),
2
2
2
441