Page 626 - Book Hosokawa Nanoparticle Technology Handbook
P. 626
APPLICATIONS 42 FABRICATION TECHNIQUE OF ORGANIC NANOCRYSTALS
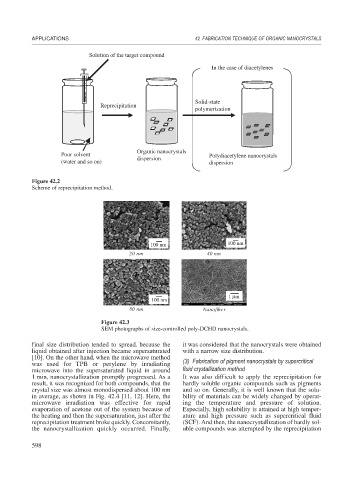
Solution of the target compound
In the case of diacetylenes
Solid-state
Reprecipitation
polymerization
Organic nanocrystals
Poor solvent Polydiacetylene nanocrystals
dispersion
(water and so on) dispersion
Figure 42.2
Scheme of reprecipitation method.
100 nm 100 nm
20 nm 40 nm
1 μm
100 nm
80 nm Nanofiber
Figure 42.3
SEM photographs of size-controlled poly-DCHD nanocrystals.
final size distribution tended to spread, because the it was considered that the nanocrystals were obtained
liquid obtained after injection became supersaturated with a narrow size distribution.
[10]. On the other hand, when the microwave method
was used for TPB or perylene by irradiating (3) Fabrication of pigment nanocrystals by supercritical
microwave into the supersaturated liquid in around fluid crystallization method
1 min, nanocrystallization promptly progressed. As a It was also difficult to apply the reprecipitation for
result, it was recognized for both compounds, that the hardly soluble organic compounds such as pigments
crystal size was almost monodispersed about 100 nm and so on. Generally, it is well known that the solu-
in average, as shown in Fig. 42.4 [11, 12]. Here, the bility of materials can be widely changed by operat-
microwave irradiation was effective for rapid ing the temperature and pressure of solution.
evaporation of acetone out of the system because of Especially, high solubility is attained at high temper-
the heating and then the supersaturation, just after the ature and high pressure such as supercritical fluid
reprecipitation treatment broke quickly. Concomitantly, (SCF). And then, the nanocrystallization of hardly sol-
the nanocrystallization quickly occurred. Finally, uble compounds was attempted by the reprecipitation
598