Page 622 - Book Hosokawa Nanoparticle Technology Handbook
P. 622
APPLICATIONS 41 SURFACE MODIFICATION OF INORGANIC NANOPARTICLES BY ORGANIC FUNCTIONAL GROUPS
Table 41.1
Functions of metal oxides arranged by inputs and outputs.
Input\output Photonic Electronic Magnet Thermal Chemical
Photonic Luminescence Photoconductivity Photoinduced Photo catalysis
Laser Photovoltaic effect magnet
Electronic Light-emitting Semiconductor Magnetoelectric
devices effect
Electro luminescence Dielectrics
Magnetic Faraday effect Magnetic Magnetic
induction heating
Colossal magnetic
resistance
Thermal Piezoelectric Magnetic phase
materials transition
Chemical Fuel cell
Chemical sensor Catalysis
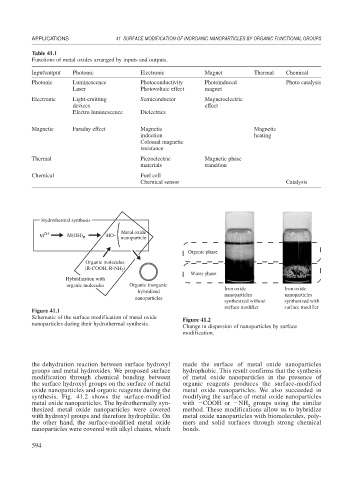
Hydrothermal synthesis
n+ Metal oxide
M M(OH) n HO– nanoparticle
Organic phase
Organic molecules
(R-COOH, R-NH )
2
Water phase
Hybridization with
organic molecules Organic-inorganic
hybridized Iron oxide Iron oxide
nanoparticles nanoparticles
nanoparticles
synthesized without synthesized with
surface modifier surface modifier
Figure 41.1
Schematic of the surface modification of metal oxide Figure 41.2
nanoparticles during their hydrothermal synthesis.
Change in dispersion of nanoparticles by surface
modification.
the dehydration reaction between surface hydroxyl made the surface of metal oxide nanoparticles
groups and metal hydroxides. We proposed surface hydrophobic. This result confirms that the synthesis
modification through chemical bonding between of metal oxide nanoparticles in the presence of
the surface hydroxyl groups on the surface of metal organic reagents produces the surface-modified
oxide nanoparticles and organic reagents during the metal oxide nanoparticles. We also succeeded in
synthesis. Fig. 41.2 shows the surface-modified modifying the surface of metal oxide nanoparticles
metal oxide nanoparticles. The hydrothermally syn- with COOH or NH groups using the similar
2
thesized metal oxide nanoparticles were covered method. These modifications allow us to hybridize
with hydroxyl groups and therefore hydrophilic. On metal oxide nanoparticles with biomolecules, poly-
the other hand, the surface-modified metal oxide mers and solid surfaces through strong chemical
nanoparticles were covered with alkyl chains, which bonds.
594