Page 71 - Book Hosokawa Nanoparticle Technology Handbook
P. 71
FUNDAMENTALS CH. 1 BASIC PROPERTIES AND MEASURING METHODS OF NANOPARTICLES
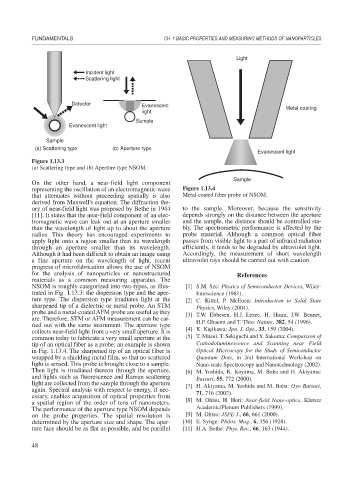
Light
Incident light
Scattering light
Detector Evanescent
light Metal coating
Sample
Evanescent light
Sample
(a) Scattering type (b) Aperture type
Evanescent light
Figure 1.13.3
(a) Scattering type and (b) Aperture type NSOM.
Sample
On the other hand, a near-field light component
representing the oscillation of an electromagnetic wave Figure 1.13.4
that attenuates without proceeding spatially is also Metal-coated fiber probe of NSOM.
derived from Maxwell’s equation. The diffraction the-
ory of near-field light was proposed by Bethe in 1944 to the sample. Moreover, because the sensitivity
[11]. It states that the near-field component of an elec- depends strongly on the distance between the aperture
tromagnetic wave can leak out at an aperture smaller and the sample, the distance should be controlled sta-
than the wavelength of light up to about the aperture bly. The spectrometric performance is affected by the
radius. This theory has encouraged experiments to probe material. Although a common optical fiber
apply light onto a region smaller than its wavelength passes from visible light to a part of infrared radiation
through an aperture smaller than its wavelength. efficiently, it tends to be degraded by ultraviolet light.
Although it had been difficult to obtain an image using Accordingly, the measurement of short wavelength
a fine aperture on the wavelength of light, recent ultraviolet rays should be carried out with caution.
progress of microfabrication allows the use of NSOM
for the analysis of nanoparticles or nanostructured References
materials as a common measuring apparatus. The
NSOM is roughly categorized into two types, as illus- [1] S.M. Sze: Physics of Semiconductor Devices, Wiley-
trated in Fig. 1.13.3: the dispersion type and the aper- Interscience (1981).
ture type. The dispersion type irradiates light at the [2] C. Kittel, P. McEuen: Introduction to Solid State
sharpened tip of a dielectric or metal probe. An STM Physics, Wiley (2004).
probe and a metal-coated AFM probe are useful as they [3] T.W. Ebbesen, H.J. Lezec, H. Hiura, J.W. Bennet,
are. Therefore, STM or AFM measurement can be car- H.F. Ghaemi and T. Thio: Nature, 382, 54 (1996).
ried out with the same instrument. The aperture type
collects near-field light from a very small aperture. It is [4] K. Kajikawa: Jpn. J. Opt., 33, 159 (2004).
common today to fabricate a very small aperture at the [5] T. Mitsui, T. Sekiguchi and Y. Sakuma: Comparison of
tip of an optical fiber as a probe: an example is shown Cathodoluminescence and Scanning near Field
in Fig. 1.13.4. The sharpened tip of an optical fiber is Optical Microscopy for the Study of Semiconductor
wrapped by a shielding metal film, so that no scattered Quantum Dots, in 2nd International Workshop on
light is sensed. This probe is brought close to a sample. Nano-scale Spectroscopy and Nanotechnology (2002).
Then light is irradiated thereon through the aperture, [6] M. Yoshida, K. Koyama, M. Baba and H. Akiyama:
and lights such as fluorescence and Raman scattering Butsuri, 55, 772 (2000).
light are collected from the sample through the aperture [7] H. Akiyama, M. Yoshida and M. Baba: Oyo Butsuri,
again. Spectral analysis with respect to energy, if nec- 71, 716 (2002).
essary, enables acquisition of optical properties from
a spatial region of the order of tens of nanometers. [8] M. Ohtsu, H. Hori: Near-field Nano-optics, Kluwer
The performance of the aperture type NSOM depends Academic/Plenum Publishers (1999).
on the probe properties. The spatial resolution is [9] M. Ohtsu: JSPE J., 66, 661 (2000).
determined by the aperture size and shape. The aper- [10] E. Synge: Philos. Mag., 6, 356 (1928).
ture face should be as flat as possible, and be parallel [11] H.A. Bethe: Phys. Rev., 66, 163 (1944).
48