Page 77 - Book Hosokawa Nanoparticle Technology Handbook
P. 77
2.1 STRUCTURE CONSTRUCTION AND FUNCTION ADAPTATION OF NANOPARTICLES FUNDAMENTALS
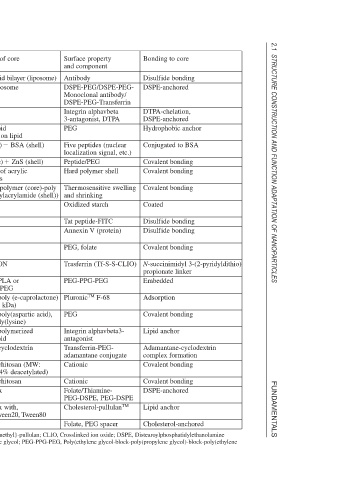
Bonding to core Disulfide bonding DSPE-anchored DTPA-chelation, DSPE-anchored Hydrophobic anchor Conjugated to BSA Covalent bonding Covalent bonding Covalent bonding Coated Disulfide bonding Disulfide bonding Covalent bonding N-succinimidyl 3-(2-pyridyldithio) propionate linker Embedded Adsorption Covalent bonding Lipid anchor Adamantane-cyclodextrin complex formation Covalent bonding Covalent bonding DSPE-anchored Lipid anchor Cholesterol-anchored
Surface property and component Antibody DSPE-PEG/DSPE-PEG- Monoclonal antibody/ DSPE-PEG-Transferrin Integrin alphavbeta 3-antagonist, DTPA PEG Five peptides (nuclear localization signal, etc.) Peptide/PEG Hard polymer shell Thermosensitive swelling and shrinking Oxidized starch Tat peptide-FITC Annexin V (protein) PEG, folate Trasferrin (Tf-S-S-CLIO) PEG-PPG-PEG F-68 Pluronic TM PEG Integrin alphavbeta3- antagonist Transferrin-PEG- adamantane conjugate Cationic Cationic Folate/Thiamine- PEG-DSPE, PEG-DSPE Cholesterol-pullulan TM Folate,
Structures of core and shell Phospholipid bilayer (liposome) Egg PC liposome Liposome Phospholipid monolayer on lipid BSA (shell) Gold (core) ZnS (shell) CdSe (core) Core-shell of acrylic terpolymers Acrylic terpolymer (core)-poly (N-isopropylacrylamide (shell)) Magnetite CLIO CLIO Magnetite CLIO, MION Matrix of PLA or PEG-PPG-PEG Matrix of poly (e-caprolactone) (MW: 14.8 kDa) Matrix of poly(aspartic acid), PLA or poly(lysine) Matrix of polymerized cationic lipid Matrix of cyclodextrin polycation Matrix of chitosan (MW: 500,000, 84% d
Typical example of nanoparticles for medical or pharmaceutical applications.
Delivery agent Magnetite Amphotericin B/ doxorubicin 90 Y Hydrophobic chelating agent of gadolinium Gold CdSe–ZnS Orally administered drugs Various drugs Clariscan (superpara-magnetite) Dextran-coated CLIO CLIO Magnetite Dextran-coated CLIO, MION Irinotecan Tamoxifen Doxorubicin/DNA Plasmid DNA (APTmu—Raf) DNA Mycobacterium phlei DNA Gadolinium–DTPA chelate Gadolinium hexanedione Plasmid DNA lipophilized with cationic lipid Hemato-porphyrin
Therapeutic purpose Hyperthermia, cancer diagnosis Passive and active targeting Target radiotherapy Cancer neutron capture therapy Intracellular diagnostics, therapeutic delivery Disease-sensing, drug delivery Controlled release from microcapsules Thermosensitive release from microcapsules MRI, hyperfusion region visualization, angiogenesis Cell-based therapy, cell labeling MRI of apoptosis (phosphatidyl serine recognition) MRI, hyperthermia, magnetic field-assisted radionuclide therapy MRI, detection of gene expression Passive drug-targeting Pas
Table 2.1.1 a b Hollow c d e f g Core–shell h i j k l m Inorganic simple core n o p q r s Organic simple core t u v w
53