Page 52 - Neural Network Modeling and Identification of Dynamical Systems
P. 52
40 2. DYNAMIC NEURAL NETWORKS: STRUCTURES AND TRAINING METHODS
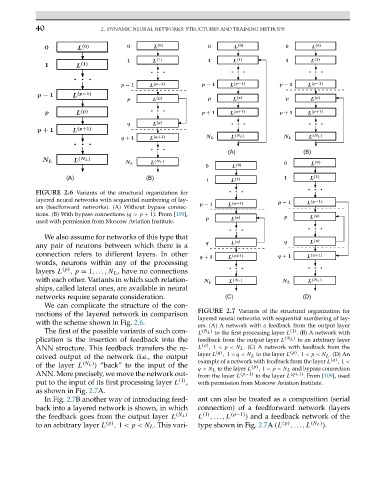
FIGURE 2.6 Variants of the structural organization for
layered neural networks with sequential numbering of lay-
ers (feedforward networks). (A) Without bypass connec-
tions. (B) With bypass connections (q> p + 1). From [109],
used with permission from Moscow Aviation Institute.
We also assume for networks of this type that
any pair of neurons between which there is a
connection refers to different layers. In other
words, neurons within any of the processing
layers L (p) ,p = 1,...,N L , have no connections
with each other. Variants in which such relation-
ships, called lateral ones, are available in neural
networks require separate consideration.
We can complicate the structure of the con-
nections of the layered network in comparison FIGURE 2.7 Variants of the structural organization for
layered neural networks with sequential numbering of lay-
with the scheme shown in Fig. 2.6.
ers. (A) A network with a feedback from the output layer
The first of the possible variants of such com- L (N L ) to the first processing layer L (1) . (B) A network with
plication is the insertion of feedback into the feedback from the output layer L (N L ) to an arbitrary layer
ANN structure. This feedback transfers the re- L (p) , 1 <p <N L . (C) A network with feedback from the
(p)
(q)
ceived output of the network (i.e., the output layer L , 1 <q <N L to the layer L , 1 <p <N L .(D) An
(q)
example of a network with feedback from the layer L
, 1 <
of the layer L (N L ) ) “back” to the input of the q< N L to the layer L (p) , 1 <p <N L and bypass connection
ANN. More precisely, we move the network out- from the layer L (p−1) to the layer L (q+1) .From[109], used
(1)
put to the input of its first processing layer L , with permission from Moscow Aviation Institute.
as shown in Fig. 2.7A.
In Fig. 2.7B another way of introducing feed- ant can also be treated as a composition (serial
back into a layered network is shown, in which connection) of a feedforward network (layers
(1)
the feedback goes from the output layer L (N L ) L ,...,L (p−1) ) and a feedback network of the
to an arbitrary layer L (p) , 1 <p <N L . This vari- type shown in Fig. 2.7A(L (p) ,...,L (N L ) ).