Page 103 - Numerical Analysis Using MATLAB and Excel
P. 103
Chapter 3 Sinusoids and Phasors
x = 3; y = 4; [theta,r] = cart2pol(x,y), deg = theta*180/pi
theta =
0.9273
r =
5
deg =
53.1301
*
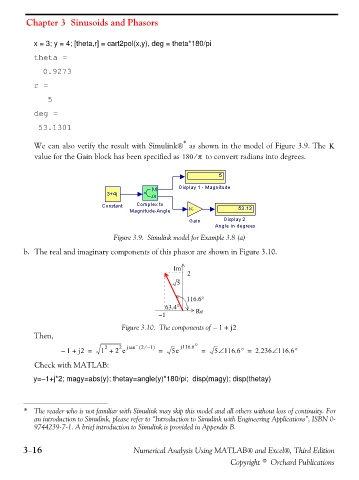
We can also verify the result with Simulink® as shown in the model of Figure 3.9. The K
value for the Gain block has been specified as 180 π⁄ to convert radians into degrees.
Figure 3.9. Simulink model for Example 3.8 (a)
b. The real and imaginary components of this phasor are shown in Figure 3.10.
Im
2
5
116.6°
63.4°
−1 Re
Figure 3.10. The components of 1 + j2
–
Then,
– ( 2 – ) j116.6°
⁄
2
2 j tan
∠
∠
– 1 + j2 = 1 + 2 e 1 = 5e = 5116.6° = 2.236 116.6°
Check with MATLAB:
y=−1+j*2; magy=abs(y); thetay=angle(y)*180/pi; disp(magy); disp(thetay)
*The reader who is not familiar with Simulink may skip this model and all others without loss of continuity. For
an introduction to Simulink, please refer to “Introduction to Simulink with Engineering Applications”, ISBN 0-
9744239-7-1. A brief introduction to Simulink is provided in Appendix B.
3−16 Numerical Analysis Using MATLAB® and Excel®, Third Edition
Copyright © Orchard Publications