Page 91 - Numerical Analysis Using MATLAB and Excel
P. 91
Chapter 3 Sinusoids and Phasors
1.25sin ( ωt – ϕ)
sin ωt
1.5
θ
1
0.75sin ( ωt + θ )
0.5
0 ωt
0
-0.5
-1
ϕ
-1.5
-4 -2 0 2 4 6 8
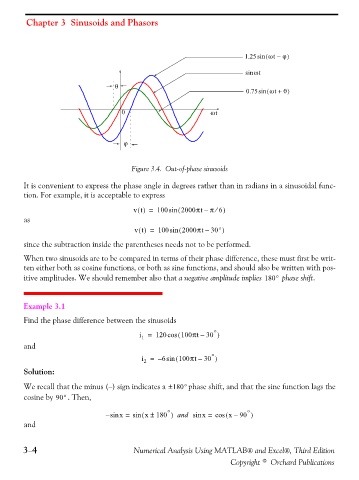
Figure 3.4. Out-of-phase sinusoids
It is convenient to express the phase angle in degrees rather than in radians in a sinusoidal func-
tion. For example, it is acceptable to express
⁄
vt() = 100sin ( 2000πt – π 6 )
as
vt() = 100sin ( 2000πt – 30° )
since the subtraction inside the parentheses needs not to be performed.
When two sinusoids are to be compared in terms of their phase difference, these must first be writ-
ten either both as cosine functions, or both as sine functions, and should also be written with pos-
itive amplitudes. We should remember also that a negative amplitude implies 180° phase shift.
Example 3.1
Find the phase difference between the sinusoids
i = 120cos ( 100πt – 30 ) °
1
and
i = – 6sin ( 100πt – 30 ) °
2
Solution:
We recall that the minus (−) sign indicates a 180°± phase shift, and that the sine function lags the
cosine by 90° . Then,
– sin x = sin ( x ± 180 ) ° and sin = cos ( x – 90 ) °
x
and
3−4 Numerical Analysis Using MATLAB® and Excel®, Third Edition
Copyright © Orchard Publications