Page 88 - Numerical Analysis Using MATLAB and Excel
P. 88
Chapter 3
Sinusoids and Phasors
T his chapter is an introduction to alternating current waveforms. The characteristics of sinu-
soids are discussed and the frequency, phase angle, and period are defined. Voltage and cur-
rent relationships are expressed in sinusoidal terms. Phasors which are rotating vectors in
terms of complex numbers, are also introduced and their relationships to sinusoids are derived.
3.1 Alternating Voltages and Currents
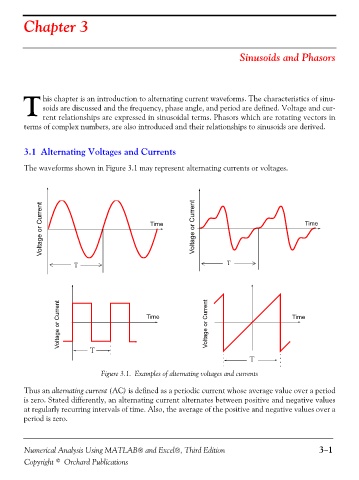
The waveforms shown in Figure 3.1 may represent alternating currents or voltages.
1 2 1
Voltage or Current 0.5 0 Time Voltage or Current 0 Time
-0.5
-2 -1
-1
T
0 2 4 6 8 10 12 0 2 T 4 6 8 10 12
Voltage or Current Time Voltage or Current Time
T
T
Figure 3.1. Examples of alternating voltages and currents
Thus an alternating current (AC) is defined as a periodic current whose average value over a period
is zero. Stated differently, an alternating current alternates between positive and negative values
at regularly recurring intervals of time. Also, the average of the positive and negative values over a
period is zero.
Numerical Analysis Using MATLAB® and Excel®, Third Edition 3−1
Copyright © Orchard Publications