Page 20 - Numerical Methods for Chemical Engineering
P. 20
Review of scalar, vector, and matrix operations 9
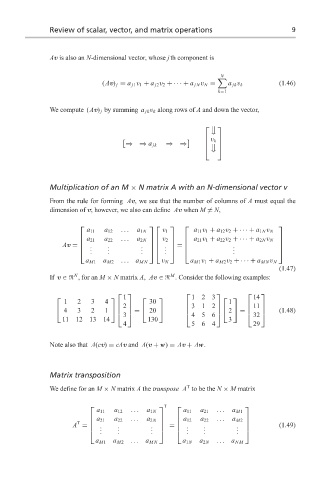
Av is also an N-dimensional vector, whose j th component is
N
(Av) j = a j1 v 1 + a j2 v 2 + ··· + a jN v N = a jk v k (1.46)
k=1
We compute (Av) j by summing a jk v k along rows of A and down the vector,
v k
⇒⇒ a jk ⇒⇒
Multiplication of an M × N matrix A with an N-dimensional vector v
From the rule for forming Av, we see that the number of columns of A must equal the
dimension of v; however, we also can define Av when M = N,
a 11 a 12 ... a 1N v 1 a 11 v 1 + a 12 v 2 + ··· + a 1N v N
a 21 a 22 a 2N v 2 a 21 v 1 + a 22 v 2 + ··· + a 2N v N
...
Av = . . .
. . . . . . = . .
.
.
. .
a M1 a M2 ... a MN v N a M1 v 1 + a M2 v 2 +· · · + a MN v N
(1.47)
M
N
If v ∈ , for an M × N matrix A, Av ∈ . Consider the following examples:
1 123 14
1 2 3 4 30 1
2 312 11
4 3 2 1 = 20 2 = (1.48)
3 456 32
11 12 13 14 130 3
4 564 29
Note also that A(cv) = cAv and A(v + w) = Av + Aw.
Matrix transposition
T
We define for an M × N matrix A the transpose A to be the N × M matrix
T
a 11 a 12 ... a 1N a 11 a 21 ... a M1
a 21 a 22 a 2N a 12 a 22 a M2
... ...
T
A = . . . = . . (1.49)
. . . . . . . . . . .
.
.
a M1 a M2 ... a MN a 1N a 2N ... a NM