Page 52 - Numerical Methods for Chemical Engineering
P. 52
Matrix factorization 41
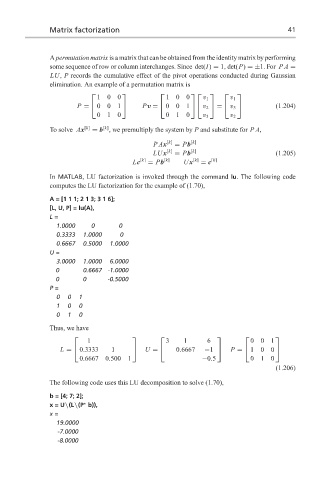
A permutation matrix is a matrix that can be obtained from the identity matrix by performing
some sequence of row or column interchanges. Since det(I) = 1, det(P) =±1. For PA =
LU, P records the cumulative effect of the pivot operations conducted during Gaussian
elimination. An example of a permutation matrix is
100 100 v 1 v 1
P = 001 Pv = 001 v 2 = v 3 (1.204)
010 010 v 3 v 2
[k]
To solve Ax [k] = b , we premultiply the system by P and substitute for PA,
PAx [k] = Pb [k]
LUx [k] = Pb [k] (1.205)
Lc [k] = Pb [k] Ux [k] = c [k]
In MATLAB, LU factorization is invoked through the command lu. The following code
computes the LU factorization for the example of (1.70),
A=[111;213;316];
[L, U, P] = lu(A),
L=
1.0000 0 0
0.3333 1.0000 0
0.6667 0.5000 1.0000
U=
3.0000 1.0000 6.0000
0 0.6667 -1.0000
0 0 -0.5000
P=
0 0 1
1 0 0
0 1 0
Thus, we have
1 3 1 6 001
L = 0.3333 1 U = 0.6667 −1 P = 100
0.6667 0.500 1 −0.5 010
(1.206)
The following code uses this LU decomposition to solve (1.70),
b = [4; 7; 2];
∗
x=U\(L\(P b)),
x=
19.0000
-7.0000
-8.0000