Page 378 - Offshore Electrical Engineering Manual
P. 378
Protection Relays 365
A B C
A
Test plug
isolation AC
supply
P 1 V
S 1
P 2
S 2
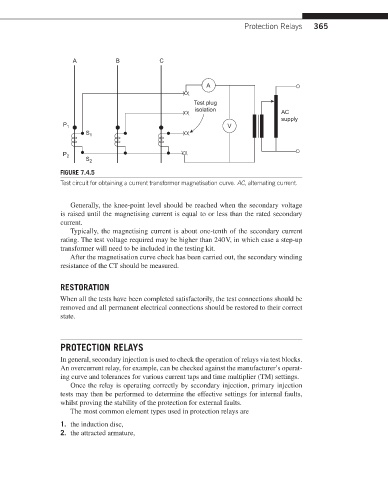
FIGURE 7.4.5
Test circuit for obtaining a current transformer magnetisation curve. AC, alternating current.
Generally, the knee-point level should be reached when the secondary voltage
is raised until the magnetising current is equal to or less than the rated secondary
current.
Typically, the magnetising current is about one-tenth of the secondary current
rating. The test voltage required may be higher than 240 V, in which case a step-up
transformer will need to be included in the testing kit.
After the magnetisation curve check has been carried out, the secondary winding
resistance of the CT should be measured.
RESTORATION
When all the tests have been completed satisfactorily, the test connections should be
removed and all permanent electrical connections should be restored to their correct
state.
PROTECTION RELAYS
In general, secondary injection is used to check the operation of relays via test blocks.
An overcurrent relay, for example, can be checked against the manufacturer’s operat-
ing curve and tolerances for various current taps and time multiplier (TM) settings.
Once the relay is operating correctly by secondary injection, primary injection
tests may then be performed to determine the effective settings for internal faults,
whilst proving the stability of the protection for external faults.
The most common element types used in protection relays are
1. the induction disc,
2. the attracted armature,