Page 24 - Optical Communications Essentials
P. 24
Basic Concepts of Communication Systems
14 Chapter One
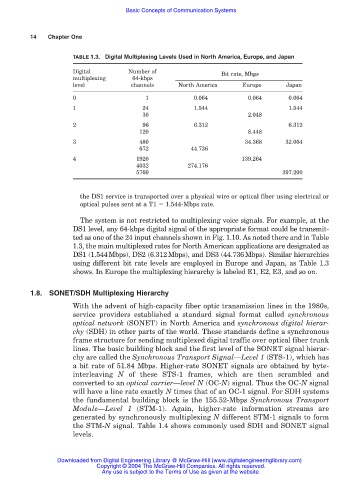
TABLE 1.3. Digital Multiplexing Levels Used in North America, Europe, and Japan
Digital Number of Bit rate, Mbps
multiplexing 64-kbps
level channels North America Europe Japan
0 1 0.064 0.064 0.064
1 24 1.544 1.544
30 2.048
2 96 6.312 6.312
120 8.448
3 480 34.368 32.064
672 44.736
4 1920 139.264
4032 274.176
5760 397.200
the DS1 service is transported over a physical wire or optical fiber using electrical or
optical pulses sent at a T1 1.544-Mbps rate.
The system is not restricted to multiplexing voice signals. For example, at the
DS1 level, any 64-kbps digital signal of the appropriate format could be transmit-
ted as one of the 24 input channels shown in Fig. 1.10. As noted there and in Table
1.3, the main multiplexed rates for North American applications are designated as
DS1 (1.544Mbps), DS2 (6.312Mbps), and DS3 (44.736Mbps). Similar hierarchies
using different bit rate levels are employed in Europe and Japan, as Table 1.3
shows. In Europe the multiplexing hierarchy is labeled E1, E2, E3, and so on.
1.8. SONET/SDH Multiplexing Hierarchy
With the advent of high-capacity fiber optic transmission lines in the 1980s,
service providers established a standard signal format called synchronous
optical network (SONET) in North America and synchronous digital hierar-
chy (SDH) in other parts of the world. These standards define a synchronous
frame structure for sending multiplexed digital traffic over optical fiber trunk
lines. The basic building block and the first level of the SONET signal hierar-
chy are called the Synchronous Transport Signal—Level 1 (STS-1), which has
a bit rate of 51.84 Mbps. Higher-rate SONET signals are obtained by byte-
interleaving N of these STS-1 frames, which are then scrambled and
converted to an optical carrier—level N (OC-N) signal. Thus the OC-N signal
will have a line rate exactly N times that of an OC-1 signal. For SDH systems
the fundamental building block is the 155.52-Mbps Synchronous Transport
Module—Level 1 (STM-1). Again, higher-rate information streams are
generated by synchronously multiplexing N different STM-1 signals to form
the STM-N signal. Table 1.4 shows commonly used SDH and SONET signal
levels.
Downloaded from Digital Engineering Library @ McGraw-Hill (www.digitalengineeringlibrary.com)
Copyright © 2004 The McGraw-Hill Companies. All rights reserved.
Any use is subject to the Terms of Use as given at the website.