Page 23 - Optical Communications Essentials
P. 23
Basic Concepts of Communication Systems
Basic Concepts of Communication Systems 13
TABLE 1.2. Examples of Information Rates for Some Typical
Voice, Video, and Data Services
Type of service Data rate
Video on demand/interactive TV 1.5 to 6Mbps
Video games 1 to 2Mbps
Remote education 1.5 to 3Mbps
Electronic shopping 1.5 to 6Mbps
Data transfer or telecommuting 1 to 3Mbps
Video conferencing 0.384 to 2Mbps
Voice (single channel) 64kbps
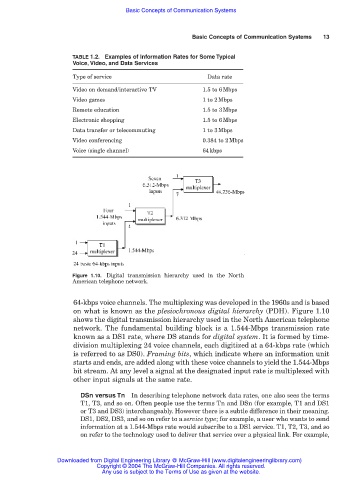
Figure 1.10. Digital transmission hierarchy used in the North
American telephone network.
64-kbps voice channels. The multiplexing was developed in the 1960s and is based
on what is known as the plesiochronous digital hierarchy (PDH). Figure 1.10
shows the digital transmission hierarchy used in the North American telephone
network. The fundamental building block is a 1.544-Mbps transmission rate
known as a DS1 rate, where DS stands for digital system. It is formed by time-
division multiplexing 24 voice channels, each digitized at a 64-kbps rate (which
is referred to as DS0). Framing bits, which indicate where an information unit
starts and ends, are added along with these voice channels to yield the 1.544-Mbps
bit stream. At any level a signal at the designated input rate is multiplexed with
other input signals at the same rate.
DSn versus Tn In describing telephone network data rates, one also sees the terms
T1, T3, and so on. Often people use the terms Tn and DSn (for example, T1 and DS1
or T3 and DS3) interchangeably. However there is a subtle difference in their meaning.
DS1, DS2, DS3, and so on refer to a service type; for example, a user who wants to send
information at a 1.544-Mbps rate would subscribe to a DS1 service. T1, T2, T3, and so
on refer to the technology used to deliver that service over a physical link. For example,
Downloaded from Digital Engineering Library @ McGraw-Hill (www.digitalengineeringlibrary.com)
Copyright © 2004 The McGraw-Hill Companies. All rights reserved.
Any use is subject to the Terms of Use as given at the website.