Page 186 - Optofluidics Fundamentals, Devices, and Applications
P. 186
Optofluidic Photonic Crystal Fibers: Pr operties and Applications 161
0
–5
0
Transmission (dB) –15 Transmission (dB) –20 800 1000 1200 1400
–10
–10
–30
–40
–20
Wavelength (nm)
–25 No grating 20.8°C
30.2°C 40.0°C
50.3°C 60.0°C
–30
1175 1200 1225 1250 1275 1300 1325 1350
Wavelength (nm)
(a)
900
0
–5 FWHM~1.1 nm 850
Transmission (dB) –10 800 Beat length (μm)
–15
750
–20
700
–25
Acoustic Acoustic
transducer damper
–30 650
830 840 850 860 870 880
Wavelength (nm)
(b)
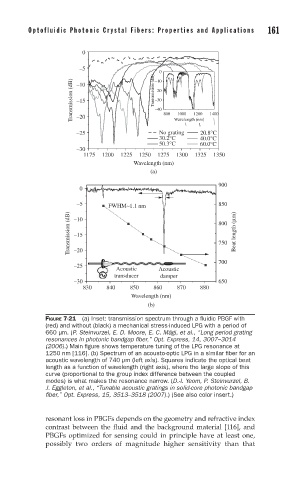
FIGURE 7-21 (a) Inset: transmission spectrum through a fl uidic PBGF with
(red) and without (black) a mechanical stress-induced LPG with a period of
660 μm. (P. Steinvurzel, E. D. Moore, E. C. Mägi, et al., “Long period grating
resonances in photonic bandgap fi ber,” Opt. Express, 14, 3007–3014
(2006).) Main fi gure shows temperature tuning of the LPG resonance at
1250 nm [116]. (b) Spectrum of an acousto-optic LPG in a similar fi ber for an
acoustic wavelength of 740 μm (left axis). Squares indicate the optical beat
length as a function of wavelength (right axis), where the large slope of this
curve (proportional to the group index difference between the coupled
modes) is what makes the resonance narrow. (D.-I. Yeom, P. Steinvurzel, B.
J. Eggleton, et al., “Tunable acoustic gratings in solid-core photonic bandgap
fi ber,” Opt. Express, 15, 3513–3518 (2007).) (See also color insert.)
resonant loss in PBGFs depends on the geometry and refractive index
contrast between the fluid and the background material [116], and
PBGFs optimized for sensing could in principle have at least one,
possibly two orders of magnitude higher sensitivity than that