Page 297 - Organic Electronics in Sensors and Biotechnology
P. 297
274 Chapter Seven
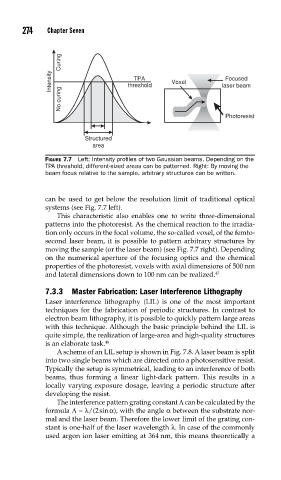
Curing
Intensity threshold Voxel laser beam
Focused
TPA
No curing
Photoresist
Structured
area
FIGURE 7.7 Left: Intensity profi les of two Gaussian beams. Depending on the
TPA threshold, different-sized areas can be patterned. Right: By moving the
beam focus relative to the sample, arbitrary structures can be written.
can be used to get below the resolution limit of traditional optical
systems (see Fig. 7.7 left).
This characteristic also enables one to write three-dimensional
patterns into the photoresist. As the chemical reaction to the irradia-
tion only occurs in the focal volume, the so-called voxel, of the femto-
second laser beam, it is possible to pattern arbitrary structures by
moving the sample (or the laser beam) (see Fig. 7.7 right). Depending
on the numerical aperture of the focusing optics and the chemical
properties of the photoresist, voxels with axial dimensions of 500 nm
and lateral dimensions down to 100 nm can be realized. 47
7.3.3 Master Fabrication: Laser Interference Lithography
Laser interference lithography (LIL) is one of the most important
techniques for the fabrication of periodic structures. In contrast to
electron beam lithography, it is possible to quickly pattern large areas
with this technique. Although the basic principle behind the LIL is
quite simple, the realization of large-area and high-quality structures
is an elaborate task. 48
A scheme of an LIL setup is shown in Fig. 7.8. A laser beam is split
into two single beams which are directed onto a photosensitive resist.
Typically the setup is symmetrical, leading to an interference of both
beams, thus forming a linear light-dark pattern. This results in a
locally varying exposure dosage, leaving a periodic structure after
developing the resist.
The interference pattern grating constant Λ can be calculated by the
formula Λ = λ/(2 sin α), with the angle α between the substrate nor-
mal and the laser beam. Therefore the lower limit of the grating con-
stant is one-half of the laser wavelength λ. In case of the commonly
used argon ion laser emitting at 364 nm, this means theoretically a