Page 330 - Organic Electronics in Sensors and Biotechnology
P. 330
Organic Electronics in Memories and Sensing Applications 307
CF 3
F 2 C
CF 3
CF 2
F 2 C F 2 C
CF 2
CF 2
F 2 C F 2 C
CF 2
CF 2
F 3 C F 2 C F 2 C
CF 2
F 2 C
Si Si Si Si
H 3 CO OCH 3 Cl Cl Cl Cl Cl Cl
Cl Cl Cl
OCH 3
PTS FPTS FOTS FDTS
OH
P
OH
O
ODPA
Me Me
H Si OMe
Me Si N Si Me C 18 H 37
OMe
Me Me
HMDS ODS
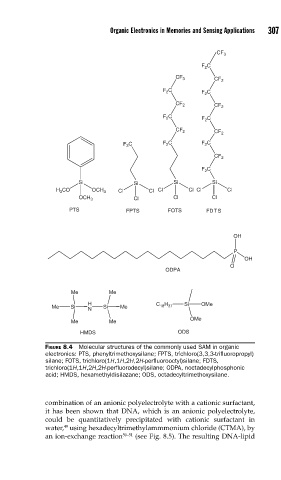
FIGURE 8.4 Molecular structures of the commonly used SAM in organic
electronics: PTS, phenyltrimethoxysilane; FPTS, trichloro(3,3,3-trifl uoropropyl)
silane; FOTS, trichloro(1H,1H,2H,2H-perfl uorooctyl)silane; FDTS,
trichloro(1H,1H,2H,2H-perfl uorodecyl)silane; ODPA, noctadecylphosphonic
acid; HMDS, hexamethyldisilazane; ODS, octadecyltrimethoxysilane.
combination of an anionic polyelectrolyte with a cationic surfactant,
it has been shown that DNA, which is an anionic polyelectrolyte,
could be quantitatively precipitated with cationic surfactant in
49
water, using hexadecyltrimethylammmonium chloride (CTMA), by
an ion-exchange reaction 50–51 (see Fig. 8.5). The resulting DNA-lipid