Page 333 - Organic Electronics in Sensors and Biotechnology
P. 333
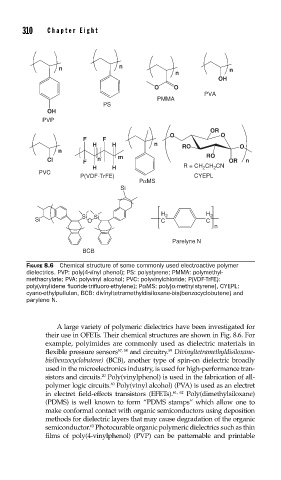
310 Cha pte r Ei g h t
n n n
n
OH
O O
PVA
PMMA
PS
OH
PVP
OR
O O
F F
H H n RO O
n
Cl F n m RO OR n
H H R = CH CH CN
2
2
PVC
P(VDF-TrFE) CYEPL
PαMS
Si
H H
Si Si 2 2
Si O C C
n
Parelyne N
BCB
FIGURE 8.6 Chemical structure of some commonly used electroactive polymer
dielectrics. PVP: poly(4-vinyl phenol); PS: polystyrene; PMMA: polymethyl-
methacrylate; PVA: polyvinyl alcohol; PVC: polyvinylchloride; P(VDF-TrFE):
poly(vinylidene fl uoride-trifl uoro-ethylene); PαMS: poly[α-methylstyrene], CYEPL:
cyano-ethylpullulan, BCB: divinyltetramethyldisiloxane-bis(benzocyclobutene) and
parylene N.
A large variety of polymeric dielectrics have been investigated for
their use in OFETs. Their chemical structures are shown in Fig. 8.6. For
example, polyimides are commonly used as dielectric materials in
flexible pressure sensors 57, 58 and circuitry. Divinyltetramethyldisiloxane-
59
bis(benzocyclobutene) (BCB), another type of spin-on dielectric broadly
used in the microelectronics industry, is used for high-performance tran-
20
sistors and circuits. Poly(vinylphenol) is used in the fabrication of all-
polymer logic circuits. Poly(vinyl alcohol) (PVA) is used as an electret
60
in electret field-effects transistors (EFETs). 61, 62 Poly(dimethylsiloxane)
(PDMS) is well known to form “PDMS stamps” which allow one to
make conformal contact with organic semiconductors using deposition
methods for dielectric layers that may cause degradation of the organic
63
semiconductor. Photocurable organic polymeric dielectrics such as thin
films of poly(4-vinylphenol) (PVP) can be patternable and printable