Page 331 - Organic Electronics in Sensors and Biotechnology
P. 331
308 Cha pte r Ei g h t
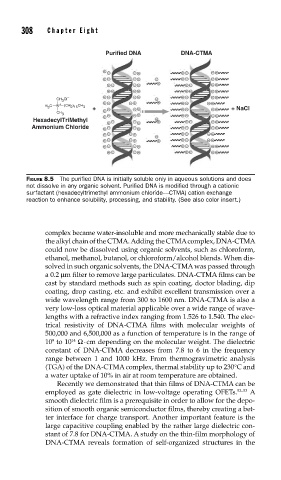
Purified DNA DNA-CTMA
–
CH Cl
3
H C N + (CH ) 2 15 CH 3
3 + + NaCl
CH
3
HexadecylTriMethyl
Ammonium Chloride
FIGURE 8.5 The purifi ed DNA is initially soluble only in aqueous solutions and does
not dissolve in any organic solvent. Purifi ed DNA is modifi ed through a cationic
surfactant (hexadecyltrimethyl ammonium chloride––CTMA) cation exchange
reaction to enhance solubility, processing, and stability. (See also color insert.)
complex became water-insoluble and more mechanically stable due to
the alkyl chain of the CTMA. Adding the CTMA complex, DNA-CTMA
could now be dissolved using organic solvents, such as chloroform,
ethanol, methanol, butanol, or chloroform/alcohol blends. When dis-
solved in such organic solvents, the DNA-CTMA was passed through
a 0.2 μm filter to remove large particulates. DNA-CTMA films can be
cast by standard methods such as spin coating, doctor blading, dip
coating, drop casting, etc. and exhibit excellent transmission over a
wide wavelength range from 300 to 1600 nm. DNA-CTMA is also a
very low-loss optical material applicable over a wide range of wave-
lengths with a refractive index ranging from 1.526 to 1.540. The elec-
trical resistivity of DNA-CTMA films with molecular weights of
500,000 and 6,500,000 as a function of temperature is in the range of
9
14
10 to 10 Ω . cm depending on the molecular weight. The dielectric
constant of DNA-CTMA decreases from 7.8 to 6 in the frequency
range between 1 and 1000 kHz. From thermogravimetric analysis
(TGA) of the DNA-CTMA complex, thermal stability up to 230°C and
a water uptake of 10% in air at room temperature are obtained.
Recently we demonstrated that thin films of DNA-CTMA can be
employed as gate dielectric in low-voltage operating OFETs. 52–53 A
smooth dielectric film is a prerequisite in order to allow for the depo-
sition of smooth organic semiconductor films, thereby creating a bet-
ter interface for charge transport. Another important feature is the
large capacitive coupling enabled by the rather large dielectric con-
stant of 7.8 for DNA-CTMA. A study on the thin-film morphology of
DNA-CTMA reveals formation of self-organized structures in the