Page 393 - Organic Electronics in Sensors and Biotechnology
P. 393
370 Chapter Ten
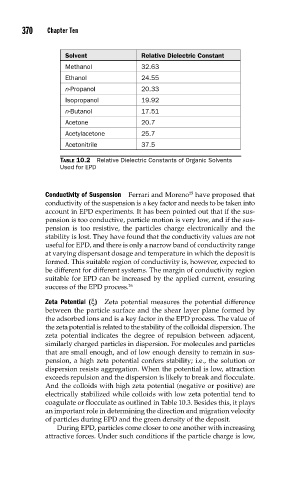
Solvent Relative Dielectric Constant
Methanol 32.63
Ethanol 24.55
n-Propanol 20.33
Isopropanol 19.92
n-Butanol 17.51
Acetone 20.7
Acetylacetone 25.7
Acetonitrile 37.5
TABLE 10.2 Relative Dielectric Constants of Organic Solvents
Used for EPD
25
Conductivity of Suspension Ferrari and Moreno have proposed that
conductivity of the suspension is a key factor and needs to be taken into
account in EPD experiments. It has been pointed out that if the sus-
pension is too conductive, particle motion is very low, and if the sus-
pension is too resistive, the particles charge electronically and the
stability is lost. They have found that the conductivity values are not
useful for EPD, and there is only a narrow band of conductivity range
at varying dispersant dosage and temperature in which the deposit is
formed. This suitable region of conductivity is, however, expected to
be different for different systems. The margin of conductivity region
suitable for EPD can be increased by the applied current, ensuring
success of the EPD process. 26
Zeta Potential (ξ) Zeta potential measures the potential difference
between the particle surface and the shear layer plane formed by
the adsorbed ions and is a key factor in the EPD process. The value of
the zeta potential is related to the stability of the colloidal dispersion. The
zeta potential indicates the degree of repulsion between adjacent,
similarly charged particles in dispersion. For molecules and particles
that are small enough, and of low enough density to remain in sus-
pension, a high zeta potential confers stability; i.e., the solution or
dispersion resists aggregation. When the potential is low, attraction
exceeds repulsion and the dispersion is likely to break and flocculate.
And the colloids with high zeta potential (negative or positive) are
electrically stabilized while colloids with low zeta potential tend to
coagulate or flocculate as outlined in Table 10.3. Besides this, it plays
an important role in determining the direction and migration velocity
of particles during EPD and the green density of the deposit.
During EPD, particles come closer to one another with increasing
attractive forces. Under such conditions if the particle charge is low,