Page 88 - Organic Electronics in Sensors and Biotechnology
P. 88
Or ganic Thin-Film Transistors for Inor ganic Substance Monitoring 65
the decomposition temperature was investigated by DSC analysis,
evidencing only fusion occurs at 247.1°C.
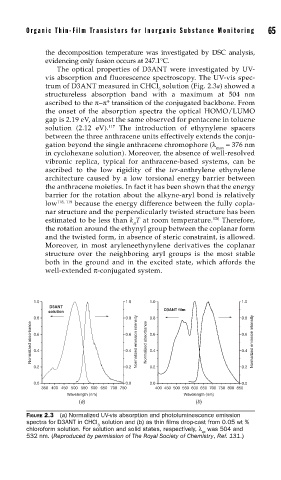
The optical properties of D3ANT were investigated by UV-
vis absorption and fluorescence spectroscopy. The UV-vis spec-
trum of D3ANT measured in CHCl solution (Fig. 2.3a) showed a
3
structureless absorption band with a maximum at 504 nm
ascribed to the π−π* transition of the conjugated backbone. From
the onset of the absorption spectra the optical HOMO/LUMO
gap is 2.19 eV, almost the same observed for pentacene in toluene
117
solution (2.12 eV). The introduction of ethynylene spacers
between the three anthracene units effectively extends the conju-
gation beyond the single anthracene chromophore (λ = 376 nm
max
in cyclohexane solution). Moreover, the absence of well-resolved
vibronic replica, typical for anthracene-based systems, can be
ascribed to the low rigidity of the ter-anthrylene ethynylene
architecture caused by a low torsional energy barrier between
the anthracene moieties. In fact it has been shown that the energy
barrier for the rotation about the alkyne-aryl bond is relatively
low 118, 119 because the energy difference between the fully copla-
nar structure and the perpendicularly twisted structure has been
120
estimated to be less than k T at room temperature. Therefore,
B
the rotation around the ethynyl group between the coplanar form
and the twisted form, in absence of steric constraint, is allowed.
Moreover, in most aryleneethynylene derivatives the coplanar
structure over the neighboring aryl groups is the most stable
both in the ground and in the excited state, which affords the
well-extended π-conjugated system.
1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0
D3ANT
solution D3ANT film
0.8 0.8 0.8 0.8
Normalized absorbance 0.6 0.6 Normalized emission intensity Normalized absorbance 0.6 0.6 Normalized emission intensity
0.4
0.4
0.4
0.4
0.2 0.2 0.2 0.2
0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0
350 400 450 500 550 600 650 700 750 400 450 500 550 600 650 700 750 800 850
Wavelength (nm) Wavelength (nm)
(a) (b)
FIGURE 2.3 (a) Normalized UV-vis absorption and photoluminescence emission
spectra for D3ANT in CHCl solution and (b) as thin fi lms drop-cast from 0.05 wt %
3
chloroform solution. For solution and solid states, respectively, λ was 504 and
ex
532 nm. (Reproduced by permission of The Royal Society of Chemistry, Ref. 131.)