Page 283 - Petroleum and Gas Field Processing
P. 283
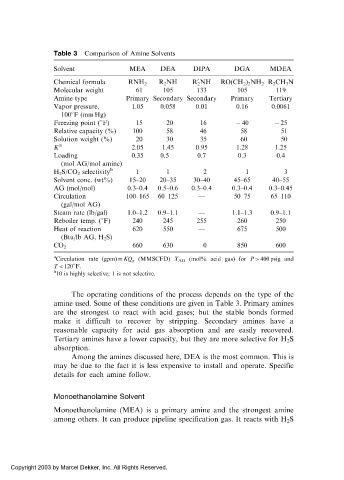
Table 3 Comparison of Amine Solvents
Solvent MEA DEA DIPA DGA MDEA
Chemical formula RNH 2 R 2 NH R 2 NH RO(CH 2 ) 2 NH 2 R 2 CH 3 N
0
Molecular weight 61 105 133 105 119
Amine type Primary Secondary Secondary Primary Tertiary
Vapor pressure, 1.05 0.058 0.01 0.16 0.0061
100 F (mm Hg)
Freezing point ( F) 15 20 16 40 25
Relative capacity (%) 100 58 46 58 51
Solution weight (%) 20 30 35 60 50
K a 2.05 1.45 0.95 1.28 1.25
Loading 0.35 0.5 0.7 0.3 0.4
(mol AG/mol amine)
H 2 S/CO 2 selectivity b 1 1 2 1 3
Solvent conc. (wt%) 15–20 20–35 30–40 45–65 40–55
AG (mol/mol) 0.3–0.4 0.5–0.6 0.3–0.4 0.3–0.4 0.3–0.45
Circulation 100–165 60–125 — 50–75 65–110
(gal/mol AG)
Steam rate (lb/gal) 1.0–1.2 0.9–1.1 — 1.1–1.3 0.9–1.1
Reboiler temp. ( F) 240 245 255 260 250
Heat of reaction 620 550 — 675 500
(Btu/lb AG, H 2 S)
660 630 0 850 600
CO 2
a
Circulation rate (gpm) ¼ KQ g (MMSCFD) X AG (mol% acid gas) for P > 400 psig and
T < 120 F.
b
10 is highly selective; 1 is not selective.
The operating conditions of the process depends on the type of the
amine used. Some of these conditions are given in Table 3. Primary amines
are the strongest to react with acid gases; but the stable bonds formed
make it difficult to recover by stripping. Secondary amines have a
reasonable capacity for acid gas absorption and are easily recovered.
Tertiary amines have a lower capacity, but they are more selective for H 2 S
absorption.
Among the amines discussed here, DEA is the most common. This is
may be due to the fact it is less expensive to install and operate. Specific
details for each amine follow.
Monoethanolamine Solvent
Monoethanolamine (MEA) is a primary amine and the strongest amine
among others. It can produce pipeline specification gas. It reacts with H 2 S
Copyright 2003 by Marcel Dekker, Inc. All Rights Reserved.