Page 201 - Petrophysics 2E
P. 201
174 PETROPHYSICS: RESERVOIR ROCK PROPERTIES
30 120
6r 25
8 20
6 15
8
L 4oz
10
5 20 1
v
0 0
-10 12 14 16 18 20 22 24 26 28t
Porosity, %
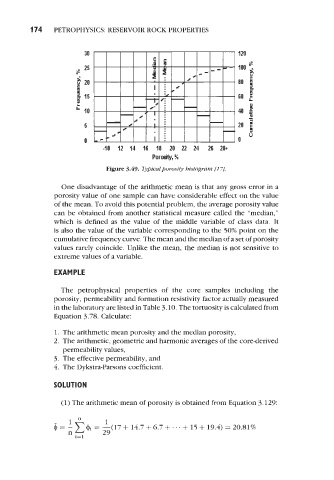
Figure 3.49. Typiealporo&y histogram (1 71,
One disadvantage of the arithmetic mean is that any gross error in a
porosity value of one sample can have considerable effect on the value
of the mean. To avoid this potential problem, the average porosity value
can be obtained from another statistical measure called the “median,”
which is defined as the value of the middle variable of class data. It
is also the value of the variable corresponding to the 50% point on the
cumulative frequency curve. The mean and the median of a set of porosity
values rarely coincide. Unlike the mean, the median is not sensitive to
extreme values of a variable.
EXAMPLE
The petrophysical properties of the core samples including the
porosity, permeability and formation resistivity factor actually measured
in the laboratory are listed in Table 3.10. The tortuosity is calculated from
Equation 3.78. Calculate:
1. The arithmetic mean porosity and the median porosity,
2. The arithmetic, geometric and harmonic averages of the corederived
permeability values,
3. The effective permeability, and
4. The Dykstra-Parsons coefficient.
SOLUTION
(1) The arithmetic mean of porosity is obtained from Equation 3.129:
1 1
6 = - @. - -(17 + 14.7 + 6.7 + . . + 15 + 19.4) = 20.81%
- 29
i=l