Page 590 - Petrophysics
P. 590
STATIC STRESSSTRAIN RELATION 557
Y
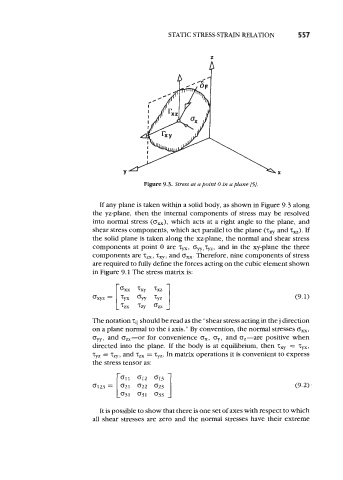
Figum 9.3. Stress at a point 0 in a plane f5j.
If any plane is taken within a solid body, as shown in Figure 9.3 along
the yz-plane, then the internal components of stress may be resolved
into normal stress (on), which acts at a right angle to the plane, and
shear stress components, which act parallel to the plane (zxy and zxz). If
the solid plane is taken along the xz-plane, the normal and shear stress
components at point 0 are zy., ow,zyz, and in the xy-plane the three
components are zm , zq, and 0,. Therefore, nine components of stress
are required to fully define the forces acting on the cubic element shown
in Figure 9.1 The stress matrix is:
The notation Tij should be read as the “shear stress acting in the j direction
on a plane norma1 to the i axis.” By convention, the normal stresses o,,
ow, and oZ-or for convenience ox, oY, and 0,-are positive when
directed into the plane. If the body is at equilibrium, then zq = zyx,
T~ = ’tV, and 7% = zyz. In matrix operations it is convenient to express
the stress tensor as:
It is possible to show that there is one set of axes with respect to which
all shear stresses are zero and the normal stresses have their extreme