Page 591 - Petrophysics
P. 591
558 PETROPHYSICS: RESERVOIR ROCK PROPERTIES
Maxi mum
Principal Stress
1
(u,
Stress Vector
Intermediate
MI ni mu m Principal Stress
Principal Stress ( u* 1
(U3)
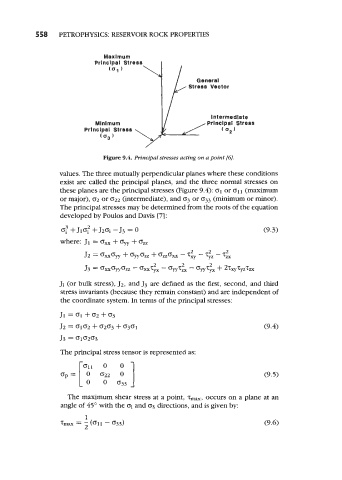
Figure 9.4. Principal stresses actlng on a point [GI.
values. The three mutually perpendicular planes where these conditions
exist are called the principal planes, and the three normal stresses on
these planes are the principal stresses (Figure 9.4): 01 or 011 (maximum
or major), 02 or 022 (intermediate), and 03 or 033 (minimum or minor).
The principal stresses may be determined from the roots of the equation
developed by Poulos and Davis [7] :
0: +JIG; + J2Oi - 53 = 0 (9.3)
where: J1 = on + ow + bZz
2 2 2
52 = OnOyy + OyyOzz + OzzOm - Tw - Tyz - T,
2 2 2
J3 = OxxOyyOzz - OxxTyx - OyyZvr - OyyTyx + 2TxyTyzTvr
JI (or bulk stress), J2, and 53 are defined as the first, second, and third
stress invariants (because they remain constant) and are independent of
the coordinate system. In terms of the principal stresses:
(9.4)
The principal stress tensor is represented as:
0
(9.5)
0 033
,
The maximum shear stress at a point, T ~ occurs on a plane at an
~
angle of 45" with the 01 and 63 directions, and is given by: