Page 58 - Photodetection and Measurement - Maximizing Performance in Optical Systems
P. 58
Fundamental Noise Basics and Calculations
Fundamental Noise Basics and Calculations 51
TABLE 3.2 Thermal Noise Voltages
Resistance Thermal noise voltage density
50W 0.89nV/ Hz
1kW 4nV/ Hz
1MW 126nV/ Hz
1GW 4mV/ Hz
Leakage
(dark current)
I p
V b 30nA
R L - Photocurrent
- Thermal noise of load resistor
- Shot noise of dark current
- Shot noise of photocurrent
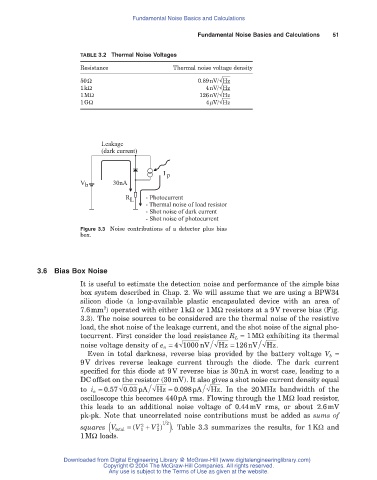
Figure 3.3 Noise contributions of a detector plus bias
box.
3.6 Bias Box Noise
It is useful to estimate the detection noise and performance of the simple bias
box system described in Chap. 2. We will assume that we are using a BPW34
silicon diode (a long-available plastic encapsulated device with an area of
2
7.6mm ) operated with either 1kW or 1MW resistors at a 9V reverse bias (Fig.
3.3). The noise sources to be considered are the thermal noise of the resistive
load, the shot noise of the leakage current, and the shot noise of the signal pho-
tocurrent. First consider the load resistance R L = 1MW exhibiting its thermal
noise voltage density of e n = 4 1000 nV Hz = 126nV Hz .
Even in total darkness, reverse bias provided by the battery voltage V b =
9V drives reverse leakage current through the diode. The dark current
specified for this diode at 9V reverse bias is 30nA in worst case, leading to a
DC offset on the resistor (30mV). It also gives a shot noise current density equal
.
to i n = 0 57 0 03. . pA Hz = 0 098pA Hz . In the 20MHz bandwidth of the
oscilloscope this becomes 440pA rms. Flowing through the 1MW load resistor,
this leads to an additional noise voltage of 0.44mV rms, or about 2.6mV
pk-pk. Note that uncorrelated noise contributions must be added as sums of
(
12
squares V total = ( V + V ) ) . Table 3.3 summarizes the results, for 1KW and
2
2
2
1
1MW loads.
Downloaded from Digital Engineering Library @ McGraw-Hill (www.digitalengineeringlibrary.com)
Copyright © 2004 The McGraw-Hill Companies. All rights reserved.
Any use is subject to the Terms of Use as given at the website.