Page 207 - Photonics Essentials an introduction with experiments
P. 207
Optical Fibers and Optical Fiber Amplifiers
Optical Fibers and Optical FIber Amplifiers 201
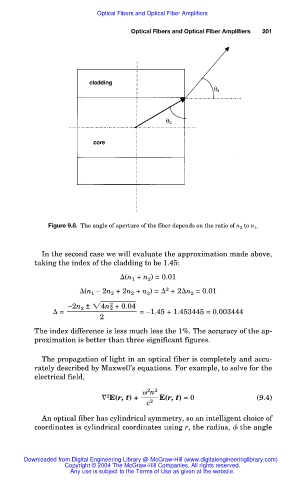
Figure 9.8. The angle of aperture of the fiber depends on the ratio of n 2 to n 1 .
In the second case we will evaluate the approximation made above,
taking the index of the cladding to be 1.45:
(n 1 + n 2 ) = 0.01
2
(n 1 – 2n 2 + 2n 2 + n 2 ) = + 2 n 2 = 0.01
–2n 2 ± 4 n 2 + 0 .0 4
2
= = –1.45 + 1.453445 = 0.003444
2
The index difference is less much less the 1%. The accuracy of the ap-
proximation is better than three significant figures.
The propagation of light in an optical fiber is completely and accu-
rately described by Maxwell’s equations. For example, to solve for the
electrical field,
2 2
n
2
E(r, t) + E(r, t) = 0 (9.4)
c 2
An optical fiber has cylindrical symmetry, so an intelligent choice of
coordinates is cylindrical coordinates using r, the radius, the angle
Downloaded from Digital Engineering Library @ McGraw-Hill (www.digitalengineeringlibrary.com)
Copyright © 2004 The McGraw-Hill Companies. All rights reserved.
Any use is subject to the Terms of Use as given at the website.