Page 249 - Physical Principles of Sedimentary Basin Analysis
P. 249
7.12 Lithospheric extension and decompression melting 231
0
ΔT
20 1 z 1
z 2
40 melt
depth [km] 60 z liquidus
80 3
100 solidus
120
0 500 1000 1500 2000
temperature [°C]
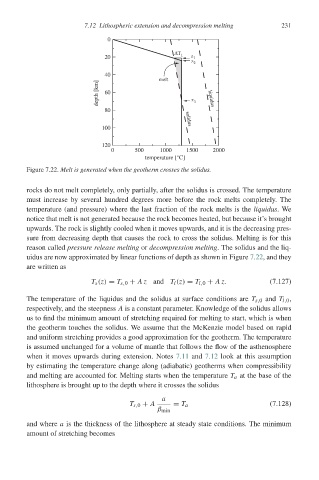
Figure 7.22. Melt is generated when the geotherm crosses the solidus.
rocks do not melt completely, only partially, after the solidus is crossed. The temperature
must increase by several hundred degrees more before the rock melts completely. The
temperature (and pressure) where the last fraction of the rock melts is the liquidus.We
notice that melt is not generated because the rock becomes heated, but because it’s brought
upwards. The rock is slightly cooled when it moves upwards, and it is the decreasing pres-
sure from decreasing depth that causes the rock to cross the solidus. Melting is for this
reason called pressure release melting or decompression melting. The solidus and the liq-
uidus are now approximated by linear functions of depth as shown in Figure 7.22, and they
are written as
T s (z) = T s,0 + Az and T l (z) = T l,0 + Az. (7.127)
The temperature of the liquidus and the solidus at surface conditions are T s,0 and T l,0 ,
respectively, and the steepness A is a constant parameter. Knowledge of the solidus allows
us to find the minimum amount of stretching required for melting to start, which is when
the geotherm touches the solidus. We assume that the McKenzie model based on rapid
and uniform stretching provides a good approximation for the geotherm. The temperature
is assumed unchanged for a volume of mantle that follows the flow of the asthenosphere
when it moves upwards during extension. Notes 7.11 and 7.12 look at this assumption
by estimating the temperature change along (adiabatic) geotherms when compressibility
and melting are accounted for. Melting starts when the temperature T a at the base of the
lithosphere is brought up to the depth where it crosses the solidus
a
T s,0 + A = T a (7.128)
β min
and where a is the thickness of the lithosphere at steady state conditions. The minimum
amount of stretching becomes