Page 33 - Physical chemistry eng
P. 33
10 CHAPTER 1 Fundamental Concepts of Thermodynamics
Solution
The number of moles of He, Ne, and Xe is given by
PV 1.50bar * 2.00L
= =
n He -2 -1 -1 = 0.121 mol
RT 8.314 * 10 L bar K mol * 298 K
PV 2.50bar * 3.00 L
= =
n Ne -2 -1 -1 = 0.303 mol
RT 8.314 * 10 L bar K mol * 298 K
PV 1.00bar * 1.00 L
n Xe = = = 0.0403 mol
-1
-2
RT 8.314 * 10 L bar K mol -1 * 298 K
n = n He + n Ne + n Xe = 0.464
The mole fractions are
n He 0.121
x He = = = 0.261
n 0.464
n Ne 0.303
x Ne = = = 0.653
n 0.464
n Xe 0.0403
x Xe = = = 0.0860
n 0.464
The total pressure is given by
(n He + n Ne + n )RT
Xe
P =
V
-1
-2
0.464 mol * 8.314 * 10 L bar K mol -1 * 298 K
=
6.00 L
= 1.92 bar
The partial pressures are given by
P He = x P = 0.261 * 1.92 bar = 0.501 bar
He
P Ne = x P = 0.653 * 1.92 bar = 1.25 bar
Ne
P Xe = x P = 0.0860 * 1.92 bar = 0.165 bar
Xe
1.5 A Brief Introduction to Real Gases
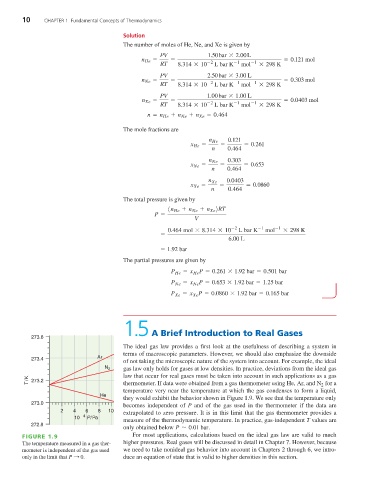
273.6
The ideal gas law provides a first look at the usefulness of describing a system in
terms of macroscopic parameters. However, we should also emphasize the downside
273.4 Ar
of not taking the microscopic nature of the system into account. For example, the ideal
N 2 gas law only holds for gases at low densities. In practice, deviations from the ideal gas
T /K 273.2 law that occur for real gases must be taken into account in such applications as a gas
for a
thermometer. If data were obtained from a gas thermometer using He, Ar, and N
2
temperature very near the temperature at which the gas condenses to form a liquid,
He
they would exhibit the behavior shown in Figure 1.9. We see that the temperature only
273.0
becomes independent of P and of the gas used in the thermometer if the data are
2 4 6 8 10 extrapolated to zero pressure. It is in this limit that the gas thermometer provides a
10 4 P/Pa
measure of the thermodynamic temperature. In practice, gas-independent T values are
272.8 '
only obtained below P 0.01 bar .
FIGURE 1.9 For most applications, calculations based on the ideal gas law are valid to much
The temperature measured in a gas ther- higher pressures. Real gases will be discussed in detail in Chapter 7. However, because
mometer is independent of the gas used we need to take nonideal gas behavior into account in Chapters 2 through 6, we intro-
only in the limit that P : 0 . duce an equation of state that is valid to higher densities in this section.