Page 144 - Pipeline Risk Management Manual Ideas, Techniques, and Resources
P. 144
Design 61121
procedural error coincident with the failure of two or more made between safety systems controlled by the pipeline
levels of safety. Industry experience shows that this is not as operator and those outside his direct control.
unlikely an occurrence as it may first appear.
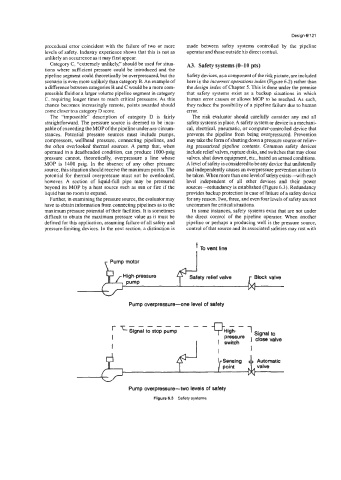
Category C, “extremely unlikely,” should be used for situa- A3. Safety systems (0-10 pts)
tions where sufficient pressure could be introduced and the
pipeline segment could theoretically be overpressured but the Safety devices, as a component of the risk picture, are included
scenario is even more unlikely than category B. An example of here in the incorrect operations index (Figure 6.2) rather than
a difference between categories B and C would be a more com- the design index of Chapter 5. This is done under the premise
pressible fluid or a larger volume pipeline segment in category that safety systems exist as a backup situations in which
C. requiring longer times to reach critical pressures. As this human error causes or allows MOP to be reached. As such,
chance becomes increasingly remote, points awarded should they reduce the possibility of a pipeline failure due to human
come closer to a category D score. error.
The “impossible” description of category D is fairly The risk evaluator should carefully consider any and all
straightforward. The pressure source is deemed to be inca- safety systems in place. A safety system or device is a mechani-
pable of exceeding the MOP ofthe pipeline under an.v circum- cal, electrical, pneumatic. or computer-controlled device that
stances. Potential pressure sources must include pumps, prevents the pipeline from being overpressured. Prevention
compressors, wellhead pressure. connecting pipelines, and may take the form of shutting down a pressure source or reliev-
the often overlooked thermal sources. A pump that, when ing pressurized pipeline contents. Common safety devices
operated in a deadheaded condition, can produce 1000-psig include relief valves, rupture disks, and switches that may close
pressure cannot, theoretically, overpressure a line whose valves, shut down equipment, etc., based on sensed conditions.
MOP is 1400 psig. In the absence of any other pressure A level of safety is considered to be any device that unilaterally
source, this situation should receive the maximum points. The and independently causes an overpressure prevention action to
potential for thermal overpressure must not be overlooked be taken. When more than one level of safety exists-with each
however. A section of liquid-full pipe may be pressured level independent of all other devices and their power
beyond its MOP by a heat source such as sun or fire if the sources-redundancy is established (Figure 6.3). Redundancy
liquid has no room to expand. provides backup protection in case of failure of a safety device
Further, in examining the pressure source, the evaluator may for any reason. Two, three, and even four levels of safety are not
have to obtain information from connecting pipelines as to the uncommon for critical situations.
maximum pressure potential of their facilities. It is sometimes In some instances, safety systems exist that are not under
difficult to obtain the maximum pressure value as it must be the direct control of the pipeline operator. When another
defined for this application, assuming failure of all safety and pipeline or perhaps a producing well is the pressure source,
pressure-limiting devices. In the next section, a distinction is control of that source and its associated safeties may rest with
t TO vent line
Pump motor I
High-pressure Safety relief valve
Pump
Pump overpressure-one level of safety
I
Pump overpressure-two levels of safety
Figure 6.3 Safety systems.