Page 185 - Pipeline Risk Management Manual Ideas, Techniques, and Resources
P. 185
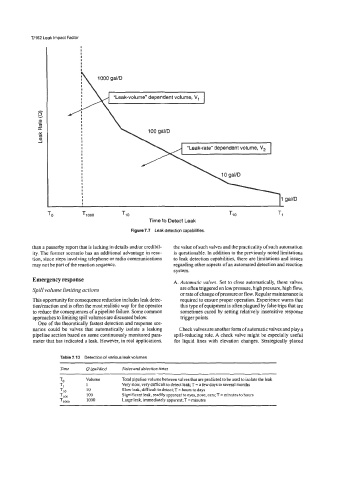
7/162 Leak Impact Factor
h
a,
*
2
Y
m
a,
J
TO Tl 000 Tl 0 Tl 0
Time to Detect Leak
Figure 7.7 Leak detection capabilities.
than a passerby report that is lacking in details and/or credibil- the value of such valves and the practicality of such automation
ity, The former scenario has an additional advantage in reac- is questionable. In addition to the previously noted limitations
tion, since steps involving telephone or radio communications to leak detection capabilities, there are limitations and issues
may not be part of the reaction sequence. regarding other aspects of an automated detection and reaction
system.
Emergency response A. Automatic valves. Set to close automatically, these valves
Spill volume limiting actions are often triggered on low pressure, high pressure, high flow,
or rate of change of pressure or flow. Regular maintenance is
lbs opportunity for consequence reduction includes leak detec- required to ensure proper operation. Experience warns that
tionheaction and is often the most realistic way for the operator this type of equipment is often plagued by false trips that are
to reduce the consequences of a pipeline failure. Some common sometimes cured by setting relatively insensitive response
approaches to limiting spill volumes are discussed below. trigger points.
One of the theoretically fastest detection and response sce-
narios could be valves that automatically isolate a leaking Check valves are another form of automatic valves and play a
pipeline section based on some continuously monitored para- spill-reducing role. A check valve might be especially useful
meter that has indicated a leak. However, in real applications, for liquid lines with elevation changes. Strategically placed
Table 7.13 Detection of various leak volumes
~~ ~
Time Q (gaNday) Notes and detection times
TO Volume Total pipeline volume between valves that are predicted to be used to isolate the leak
TI I Very slow, very difficult to detect leak; T =a few days to several months
TI0 10 Slow leak, difficult to detect; T = hours to days
TI, 100 Significant leak, readily apparent to eyes, nose, ears; T = minutes to hours
TI000 1000 Large leak, immediately apparent; T = minutes