Page 182 - Pipeline Risk Management Manual Ideas, Techniques, and Resources
P. 182
Adjustments to scores 711 59
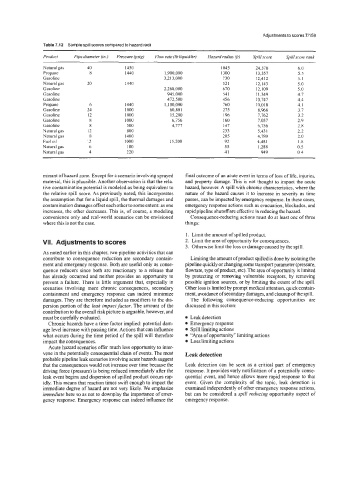
Table 7.12 Sample spill scores compared to hazard radii
Product Pipe diameter (in) Pressure (psrg) Flow rate (lb Iiquid/hr) Hazard radius ft) Spillscore Spillscore rank
Natural gas 40 1450 I045 24,370 6.0
Propane 8 1440 1,900,000 1300 13,357 5.5
Gasoline 3,213,000 730 12,412 5.1
Natural gas 20 1440 521 12,143 5.0
Gasoline 2,268,000 670 12,109 5.0
Gas o 1 in e 945,000 54 1 1 1,349 4.7
Gasoline 472,500 456 10,747 44
Propane 6 1440 1,100,000 760 10,018 4. I
Gasoline 24 1000 60,801 215 8,966 3.7
Gasoline 12 1000 15,200 I96 1,762 3.2
Gasoline 8 1000 6.756 160 7,057 2.9
Gasoline 8 500 4,777 147 6,756 28
Natural gas 12 800 233 5,431 2.2
Natural gas 8 1400 205 4,789 2.0
Fuel oil 12 1000 15.200 92 4,481 I .x
Natural gas 6 180 55 1,288 0.5
Natural gas 4 220 41 949 04
minant of hazard zone. Except for a scenario involving sprayed final outcome of an acute event in terms of loss of life, injuries.
material, this is plausible. Another observation is that the rela- and property damage. This is not thought to impact the acute
tive contamination potential is modeled as being equivalent to hazard, however. A spill with chronic characteristics, where the
the relative spill score. As previously noted, this incorporates nature of the hazard causes it to increase in severity as time
the assumption that for a liquid spill, the thermal damages and passes, can be impacted by emergency response. In these cases,
contamination damages offset eachother to some extent: as one emergency response actions such as evacuation, blockades, and
increases, the other decreases. This is, of course, a modeling rapid pipeline shutoff are effective in reducing the hazard.
convenience only and real-world scenarios can be envisioned Consequence-reducing actions must do at least one of three
where this is not the case. things:
1. Limit the amount of spilled product.
VII. Adjustments to scores 2. Limit the area of opportunity for consequences.
3. Otherwise limit the loss or damage caused by the spill.
As noted earlier in this chapter, two pipeline activities that can
contribute to consequence reduction are secondary contain- Limiting the amount of product spilled is done by isolating the
ment and emergency response. Both are useful only as conse- pipeline quickly or changing some transport parameter (pressure,
quence reducers since both are reactionary to a release that flowrate, type of product, etc). The area of opportunity is limited
has already occurred and neither provides an opportunity to by protecting or removing vulnerable receptors, by removing
prevent a failure. There is little argument that, especially in possible ignition sources, or by limiting the extent of the spill.
scenarios involving more chronic consequences, secondary Other loss is limited by prompt medical attention, quick contain-
containment and emergency response can indeed minimize ment, avoidance of secondary damages, and cleanup ofthe spill.
damages. They are therefore included as modifiers to the dis- The following consequence-reducing opportunities are
persion portion of the leak impact factor. The amount of the discussed in this section:
contribution to the overall risk picture is arguable, however, and
must be carefully evaluated. Leak detection
Chronic hazards have a time factor implied: potential dam- Emergency response
age level increase with passing time. Actions that can influence Spill limiting actions
what occurs during the time period of the spill will therefore “Area of opportunity” limiting actions
impact the consequences. Loss limiting actions
Acute hazard scenarios offer much less opportunity to inter-
vene in the potentially consequential chain of events. The most Leak detection
probable pipeline leak scenarios involving acute hazards suggest
that the consequences would not increase over time because the Leak detection can be seen as a critical part of emergency
dnving force (pressure) is being reduced immediately after the response. It provides early notification of a potentially conse-
leak event begins and dispersion of spilled product occurs rap- quential event, and hence allows more rapid response to that
idly. This means that reaction times swift enough to impact the event. Given the complexity of the topic, leak detection is
immediate degree of hazard are not very likely. We emphasize examined independently of other emergency response actions,
immediate here so as not to downplay the importance of emer- but can be considered a spill reducing opportunity aspect of
gency response. Emergency response can indeed influence the emergency response.